Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Define the following as related to proteins:
Peptide linkage
Solution
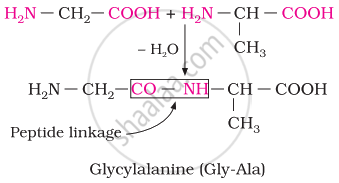
Chemically, peptide linkage is an amide formed between the –COOH group and –NH2 group. The reaction between two molecules of similar or different amino acids proceeds through the combination of the amino group of one molecule with the carboxyl group of the other. This results in the elimination of a water molecule and the formation of a peptide bond –CO–NH–. The product of the reaction is called a dipeptide because it is made up of two amino acids.
For example, when the carboxyl group of glycine combines with the amino group of alanine, we get a dipeptide, glycylalanine.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How is tripeptide formed?
What type of bonding helps in stabilising the ∝-helix structure of proteins?
Differentiate between the following :
Peptide linkage and Glycosidic linkage
The correct statement for protein haemoglobin.
Dinucleotide is obtained by joining two nucleotides together by phosphodiester linkage. Between which carbon atoms of pentose sugars of nucleotides are these linkages present?
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 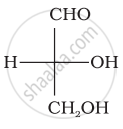 |
| (II) | 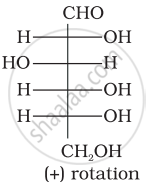 |
| (III) | 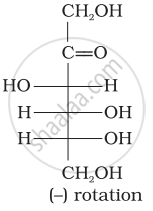 |
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by:
(i) van der Waals forces
(ii) disulphide linkage
(iii) electrostatic forces of attraction
(iv) hydrogen bonds
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of polypeptide chain into right-handed screw like structures. Which type of interactions are responsible for making the α-helix structure stable?
Assertion: β-glycosidic linkage is present in maltose,

Reason: Maltose is composed of two glucose units in which C–1 of one glucose unit is linked to C–4 of another glucose unit.
The main structural feature of proteins is
Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ______.
Out of the following, which type of interaction is responsible for the stabilisation of the α-helix structure of proteins?
The total number of negative charge in the tetrapeptide, Gly-Glu-Asp-Tyr at pH 12.5 will be ______. (Integer answers)
An α-helix is a structural feature of ______.
Assertion (A): Proteins are polymers of α-amino acids connected by a peptide bond.
Reason (R): A tetrapeptide contains 4 amino acids linked by 4 peptide bonds.
β-pleated sheet structure in proteins refers to ______.
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
