Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
Solution
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
Explanation:
Purines consist of six-membered and five-membered nitrogen-containing ring fused together.
Guanine and adenine are purine bases whose structures are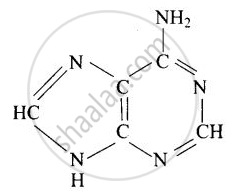
Adenine (A)
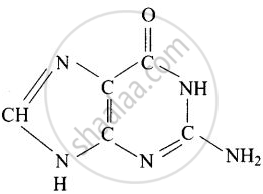
Guanine (G)
While thymine and uracil are pyrimidine bases.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Differentiate between the following :
Peptide linkage and Glycosidic linkage
The protein responsible for blood clotting is ____________.
Dinucleotide is obtained by joining two nucleotides together by phosphodiester linkage. Between which carbon atoms of pentose sugars of nucleotides are these linkages present?
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are:
(i) Insulin
(ii) Keratin
(iii) Albumin
(iv) Myosin
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by:
(i) van der Waals forces
(ii) disulphide linkage
(iii) electrostatic forces of attraction
(iv) hydrogen bonds
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of polypeptide chain into right-handed screw like structures. Which type of interactions are responsible for making the α-helix structure stable?
Which moieties of nucleosides are involved in the formation of phosphodiester linkages present in dinucleotides? What does the word diester in the name of linkage indicate? Which acid is involved in the formation of this linkage?
Explain the terms primary and secondary structure of proteins. What is the difference between α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure of proteins?
The total number of negative charge in the tetrapeptide, Gly-Glu-Asp-Tyr at pH 12.5 will be ______. (Integer answers)
β-pleated sheet structure in proteins refers to ______.
