Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What type of bonding helps in stabilising the α-helix structure of proteins?
Solution
α-Helix is one of the most common ways in which a polypeptide chain forms all possible hydrogen bonds by twisting into a right handed screw (helix) with the –NH group of each amino acid residue hydrogen bonded to the \[\begin{array}{cc}\backslash\phantom{.....}\\\ce{C=O}\\/\phantom{......}\end{array}\] of an adjacent turn of the helix.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are proteins classified on the basis of molecular shapes?
What is peptide linkage?
Define the following as related to proteins:
Peptide linkage
What are the common types of secondary structure of proteins?
Write one difference between α-helix and β-pleated structures of proteins.
The helical structure of protein is stabilized by:
Which functional group participates in disulphide bond formation in proteins?
Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz. α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure. α-helix structure of protein is stabilised by:
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 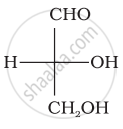 |
| (II) | 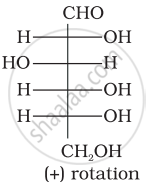 |
| (III) | 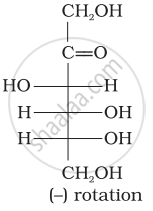 |
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are:
(i) Insulin
(ii) Keratin
(iii) Albumin
(iv) Myosin
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of polypeptide chain into right-handed screw like structures. Which type of interactions are responsible for making the α-helix structure stable?
Structures of glycine and alanine are given below. Show the peptide linkage in glycylalanine.
\[\ce{\underset{(Glycine)}{H2N - CH2 - COOH}}\];
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H2N - CH2 - COOH}\\
|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{\underset{(Alanine)}{CH3}\phantom{...}}
\end{array}\]
Explain the terms primary and secondary structure of proteins. What is the difference between α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure of proteins?
Peptide linkage is:
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheet structure.
Reason (R): The secondary structure of proteins is stabilized by hydrogen bonding.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
The total number of negative charge in the tetrapeptide, Gly-Glu-Asp-Tyr at pH 12.5 will be ______. (Integer answers)
An α-helix is a structural feature of ______.
Write a classification of proteins with an example.
