Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 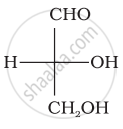 |
| (II) | 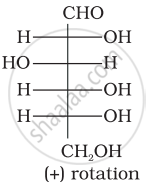 |
| (III) | 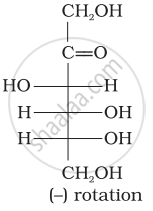 |
पर्याय
I, II, III
II, III
I, II
III
उत्तर
I, II, III
Explanation:
I, II and III structures have D configuration with –OH group on the lowest asymmetric carbon is on the right side which is comparable to (+) glyceraldehyde.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How are proteins classified on the basis of molecular shapes?
Discuss the optical activity of lactic acid.
What are the common types of secondary structure of proteins?
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by:
(i) van der Waals forces
(ii) disulphide linkage
(iii) electrostatic forces of attraction
(iv) hydrogen bonds
Assertion: β-glycosidic linkage is present in maltose,

Reason: Maltose is composed of two glucose units in which C–1 of one glucose unit is linked to C–4 of another glucose unit.
Explain the terms primary and secondary structure of proteins. What is the difference between α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure of proteins?
The main structural feature of proteins is
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheet structure.
Reason (R): The secondary structure of proteins is stabilized by hydrogen bonding.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Out of the following, which type of interaction is responsible for the stabilisation of the α-helix structure of proteins?
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
