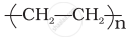Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Solutions
3: Electrochemistry
4: Chemical Kinetics
5: Surface Chemistry
6: General Principle and Processes of Isolation of Elements
7: The p-block Elements
8: The d-and f-Block Elements
9: Coordination Compounds
10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
13: Amines
14: Biomolecules
▶ 15: Polymers
16: Chemistry In Everyday Life
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 15 - Polymers NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 15 - Polymers - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 15: Polymers
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 15 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Chemistry [English] Class 12.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 15 Polymers Multiple Choice Questions (Type - I) [Pages 217 - 225]
Which of the following polymers of glucose is stored by animals?
Cellulose
Amylose
Amylopectin
Glycogen
Which of the following is not a semisynthetic polymer?
cis-polyisoprene
Cellulose nitrate
Cellulose acetate
Vulcanised rubber
The commercial name of polyacrylonitrile is ______.
Dacron
Orlon (acrilan)
PVC
Bakelite
Which of the following polymer is biodegradable?
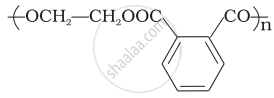
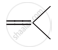
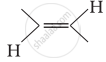
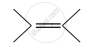
In which of the following polymers ethylene glycol is one of the monomer units?
Which of the following statements is not true about low-density polythene?
Tough
Hard
Poor conductor of electricity
Highly branched structure
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.........}\ce{CH3}\phantom{........}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{......}|\phantom{...........}|\phantom{}\\
\ce{-(CH2 - C - CH2 - C)\underset{n}{-}}\\
\phantom{......}|\phantom{...........}|\phantom{}\\
\phantom{..........}\ce{CH3}\phantom{........}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\
\end{array}\] is a polymer having monomer units:
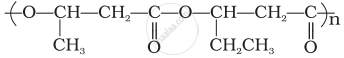
Which of the following polymer can be formed by using the following monomer unit?
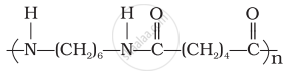
Nylon 6, 6
Nylon 2–nylon 6
Melamine polymer
Nylon-6
Which of the following polymers, need atleast one diene monomer for their preparation?
(i) Dacron
(ii) Buna-S
(iii) Neoprene
(iv) Novolac
Which of the following are characteristics of thermosetting polymers?
(i) Heavily branched cross linked polymers.
(ii) Linear slightly branched long chain molecules.
(iii) Become infusible on moulding so cannot be reused.
(iv) Soften on heating and harden on cooling, can be reused.
Which of the following polymers are thermoplastic?
(i) Teflon
(ii) Natural rubber
(iii) Neoprene
(iv) Polystyrene
Which of the following polymers are used as fibre?
(i) Polytetrafluoroethane
(ii) Polychloroprene
(iii) Nylon
(iv) Terylene
Which of the following are addition polymers?
(i) Nylon
(ii) Melamine formaldehyde resin
(iii) Orlon
(iv) Polystyrene
Which of the following polymers are condensation polymers?
(i) Bakelite
(ii) Teflon
(iii) Butyl rubber
(iv) Melamine formaldehyde resin
Which of the following monomers form biodegradable polymers?
(i) 3-hydroxybutanoic acid + 3-hydroxypentanoic acid
(ii) Glycine + amino caproic acid
(iii) Ethylene glycol + phthalic acid
(iv) Caprolactum
Which of the following are example of synthetic rubber?
(i) Polychloroprene
(ii) Polyacrylonitrile
(iii) Buna-N
(iv) cis-polyisoprene
Which of the following polymers can have strong intermolecular forces?
(i) Nylon
(ii) Polystyrene
(iii) Rubber
(iv) Polyesters
Which of the following polymers have vinylic monomer units?
(i) Acrilan
(ii) Polystyrene
(iii) Nylon
(iv) Teflon
Vulcanisation makes rubber:
(i) more elastic
(ii) soluble in inorganic solvent
(iii) crystalline
(iv) more stiff
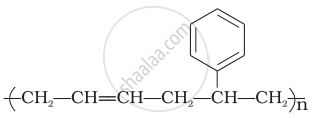
A natural linear polymer of 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene becomes hard on treatment with sulphur between 373 to 415 K and – S – S – bonds are formed between chains. Write the structure of the product of this treatment?
Identify the type of polymer.
—A—A—A—A—A—A—
Identify the type of polymer.
—A—B—B—A—A—A—B—A—
Out of chain growth polymerisation and step growth polymerisation, in which type will you place the following.

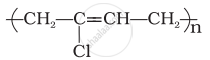
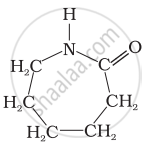
Identify the type of polymer given in the following figure.

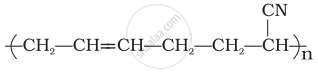
Identify the polymer given below:
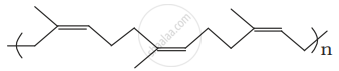
Why are rubbers called elastomers?
Can enzyme be called a polymer?
Can nucleic acids, proteins and starch be considered as step growth polymers?
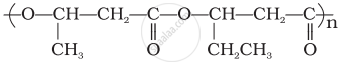
How is the following resin intermediate prepared and which polymer is formed by this monomer unit?
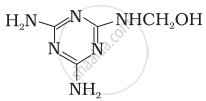
(Resin intermediate)
To have practical applications why are cross links required in rubber?
Why does cis-polyisoprene possess elastic property?
What is the structural difference between HDP and LDP? How does the structure account for different behaviour and nature, hence the use of a polymer?
What is the role of benzoyl peroxide in addition polymerisation of alkenes? Explain its mode of action with the help of an example.
Which factor imparts crystalline nature to a polymer like nylon?
Name the polymers used in laminated sheets and give the name of monomeric units involved in its formation.
Why should the monomers used in addition polymerisation through free radical pathway be very pure?
Match the polymer of column I with correct monomer of column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) High density polythene | (a) Isoprene |
| (ii) Neoprene | (b) Tetrafluoroethene |
| (iii) Natural rubber | (c) Chloroprene |
| (iv) Teflon | (d) Acrylonitrile |
| (v) Acrilan | (e) Ethene |
Match the polymers given in Column I with their chemical names given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Nylon 6 | (a) Polyvinyl chloride |
| (ii) PVC | (b) Polyacrylonitrile |
| (iii) Acrilan | (c) Polycaprolactum |
| (iv) Natural rubber | (d) Low-density polythene |
| (v) LDP | (e) cis-polyisoprene |
Match the polymers given in Column I with their commercial names given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Polyester of glycol and phthalic acid | (a) Novolac |
| (ii) Copolymer of 1, 3-butadiene and styrene | (b) Glyptal |
| (iii) Phenol and formaldehyde resin | (c) Buna-S |
| (iv) Polyester of glycol and terephthalic acid | (d) Buna-N |
| (v) Copolymer of 1, 3-butadiene and acrylonitrile | (e) Dacron |
Match the polymers given in Column I with their main applications given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Bakelite | (a) Unbreakable crockery |
| (ii) Low-density polythene | (b) Non-stick cookwares |
| (iii) Melamine-formaldehyderesin | (c) Packaging material for shock absorbance |
| (iv) Nylon 6 | (d) Electrical switches |
| (v) Polytetrafluoroethane | (e) Squeeze bottles |
| (vi) Polystyrene | (f) Tyre, cords |
Match the polymers given in Column I with the preferred mode of polymerisation followed by their monomers.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Nylon-6,6 | (a) Free radical polymerisation |
| (ii) PVC | (b) Ziegler-Natta polymerisation or coordination polymerisation |
| (iii) HDP | (c) Anionic polymerisation |
| (d) Condensation polymerisation |
Match the polymers given in Column I with the type of linkage present in them given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Terylene | (a) Glycosidic linkage |
| (ii) Nylon | (b) Ester linkage |
| (iii) Cellulose | (c) Phosphodiester linkage |
| (iv) Protein | (d) Amide linkage |
| v) RNA |
Match materials given in Column I with the polymers given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Natural rubber latex | (a) Nylon |
| (ii) Wood laminates | (b) Neoprene |
| (iii) Ropes and fibres | (c) Dacron |
| (iv) Polyester fabric | (d) Melamine formaldehyde resins |
| (v) Synthetic rubber | (e) Urea-formaldehyde resins |
| (vi) Unbreakable crockery | (f) cis-polyisoprene |
Match the polymers given in Column I with their repeating units given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Acrilan |
(a) \[\begin{array}{cc} |
| (ii) Polystyrene | (b) \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{Cl}\phantom{.......}\\ |\phantom{........}\\ \phantom{}\ce{-(CH2 - C = CH - CH2)\underset{n}{-}} \end{array}\] |
| (iii) Neoprene | (c) \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{................................}\ce{CN}\\ \phantom{..............................}|\\ \ce{-(CH2 - CH = CH - CH2 - CH2 - CH)\underset{n}{-}} \end{array}\] |
| (iv) Novolac | (d) \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{-(CH2 - CH)\underset{n}{-}}\\ \phantom{.....}|\\ \phantom{.......}\ce{CN} \end{array}\] |
| (v) Buna—N | (e) 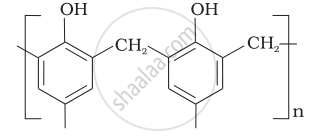 |
| (f) \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{-(CH2 - CH)\underset{n}{-}}\\ \phantom{.....}|\\ \phantom{......}\ce{Cl} \end{array}\] |
Assertion: Rayon is a semi-synthetic polymer and is taken as a better choice than cotton fabric.
Reason: Mechanical and aesthetic properties of cellulose can be improved by acetylation.
Assertion and reason both are correct statement but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statement.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Most of the Synthetic polymers are not biodegradable.
Reason: Polymerisation process induces toxic character in organic molecules.
Assertion and reason both are correct statement but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statement.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Olefinic monomers undergo addition polymerisation.
Reason: Polymerisation of vinyl chloride is initiated by peroxides/ persulphates.
Assertion and reason both are correct statement but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statement.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement
Assertion: Polyamides are best used as fibres because of high tensile strength.
Reason: Strong intermolecular forces (like hydrogen bonding within polyamides) lead to close packing of chains and increase the crystalline character, hence, provide high tensile strength to polymers
Assertion and reason both are correct statement but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statement.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion: For making rubber synthetically, isoprene molecules are polymerised.
Reason: Neoprene (a polymer of chloroprene) is a synthetic rubber.
Assertion and reason both are correct statement but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statement.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Network polymers are thermosetting.
Reason: Network polymers have high molecular mass.
Assertion and reason both are correct statement but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statement.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Polytetrafluoroethene is used in making non-stick cookwares.
Reason: Fluorine has highest electronegativity.
Assertion and reason both are correct statement but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statement.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Synthetic polymers do not degrade in the environment for a long time. How can biodegradable synthetic polymers be made. Differentiate between biopolymers and biodegradable polymers and give examples of each type.
Differentiate between rubbers and plastics on the basis of intermolecular forces.
Phenol and formaldehyde undergo condensation to give a polymar (A) which on heating with formaldehyde gives a thermosetting polymer (B). Name the polymers. Write the reactions involved in the formation of (A). What is the structural difference between two polymers?
Low density polythene and high density polythene, both are polymers of ethene but there is marked difference in their properties. Explain.
Which of the following polymers soften on heating and harden on cooling? What are the polymers with this property collectively called? What are the structural similarities between such polymers? Bakelite, urea-formaldehyde resin, polythene, polyvinyls, polystyrene.
Solutions for 15: Polymers
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 15 - Polymers NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 15 - Polymers - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 15 - Polymers
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE 15 (Polymers) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 15 Polymers are Classification of Polymers Based on Source, Types of Polymerisation Reactions - Addition Polymerisation or Chain Growth Polymerisation, Types of Polymerisation Reactions - Copolymerisation, Some Important Polymers, Types of Polymerisation Reactions - Condensation Polymerisation Or Step Growth Polymerisation, Types of Polymerisation Reactions - Rubber, Biodegradable Polymers, Classification of Polymers Based on Structure, Classification of Polymers Based on Mode of Polymerisation, Classification of Polymers Based on Molecular Forces, Classification of Polymers Based on Growth Polymerisation, Molecular Mass of Polymers, Polymers of Commercial Importance, Polymers Numericals, Introduction to Polymers.
Using NCERT Exemplar Chemistry [English] Class 12 solutions Polymers exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Chemistry [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 15, Polymers Chemistry [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.