Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Solutions
3: Electrochemistry
4: Chemical Kinetics
5: Surface Chemistry
6: General Principle and Processes of Isolation of Elements
7: The p-block Elements
8: The d-and f-Block Elements
9: Coordination Compounds
10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
▶ 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
13: Amines
14: Biomolecules
15: Polymers
16: Chemistry In Everyday Life
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 12 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Chemistry [English] Class 12.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Multiple Choice Questions (Type - I) [Pages 168 - 176]
Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of \[\ce{Hg^{2+}}\] ions as a catalyst. Which of the following products will be formed on addition of water to but-1-yne under these conditions.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{................}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{................}||\\
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - C - H}
\end{array}\]\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.......}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{.......}||\\
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - C - CH3}
\end{array}\]\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{.}||\\
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - C - OH + CO2}
\end{array}\]\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{...}\ce{O}\phantom{.............}\ce{O}\phantom{}\\
\phantom{...}||\phantom{..............}||\phantom{}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - OH + H - C - H}
\end{array}\]
Which of the following compounds is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{...}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{...}||\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - C - H}
\end{array}\]\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{.}||\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - C - CH3}
\end{array}\]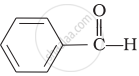
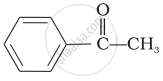
The correct order of increasing acidic strength is ______.
Phenol < Ethanol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
Ethanol < Phenol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
Ethanol < Phenol < Acetic acid < Chloroacetic acid
Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid < Phenol < Ethanol
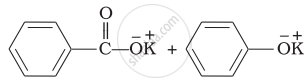
Compound \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.....}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{.....}||\\
\ce{Ph - O - C - Ph}
\end{array}\] can be prepared by the reaction of ______.
Phenol and benzoic acid in the presence of \[\ce{NaOH}\]
Phenol and benzoyl chloride in the presence of pyridine
Phenol and benzoyl chloride in the presence of \[\ce{ZnCl2}\]
Phenol and benzaldehyde in the presence of palladium
The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde.
Sodium hydrogensulphite
Phenyl hydrazine
Fehling’s solution
Grignard reagent
Cannizaro’s reaction is not given by ______.
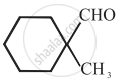
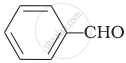
\[\ce{HCHO}\]
\[\ce{CH3CHO}\]
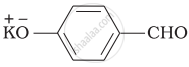
Which product is formed when the compound 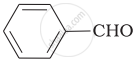 is treated with concentrated aqueous \[\ce{KOH}\] solution?
is treated with concentrated aqueous \[\ce{KOH}\] solution?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - C ≡ CH ->[40{%} H2SO4][1{%} HgSO4] A ->[Isomerisation] CH3 - C - CH3}\\
\phantom{........................................}||\\
\phantom{........................................}\ce{O}\\
\end{array}\]
Structure of ‘A’ and type of isomerism in the above reaction are respectively.
Prop–1–en–2–ol, metamerism
Prop-1-en-1-ol, tautomerism
Prop-2-en-2-ol, geometrical isomerism
Prop-1-en-2-ol, tautomerism
Compounds A and C in the following reaction are:
\[\ce{CH3CHO ->[(i) CH3MgBr][(ii) H2O] (A) ->[H2SO4, Δ] (B) ->[Hydroboration oxidation] (C)}\]
identical
positional isomers
functional isomers
optical isomers
Which is the most suitable reagent for the following conversion?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{....................}\ce{O}\phantom{.....................................}\ce{O}\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{....................}||\phantom{......................................}||\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - CH = CH - CH2 - C - CH3 -> CH3 - CH = CH - CH2 - C - OH}\phantom{.}
\end{array}\]
Tollen’s reagent
Benzoyl peroxide
\[\ce{I2}\] and \[\ce{NaOH}\] solution
\[\ce{Sn}\] and \[\ce{NaOH}\] solution
Which of the following compounds will give butanone on oxidation with alkaline \[\ce{KMnO4}\] solution?
Butan-1-ol
Butan-2-ol
Both of these
None of these
In Clemmensen Reduction carbonyl compound is treated with:
Zinc amalgam + HCl
Sodium amalgam + HCl
Zinc amalgam + nitric acid
Sodium amalgam + HNO3
Which of the following compounds do not undergo aldol condensation?
(i) \[\ce{CH3 - CHO}\]
(ii) 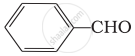
(iii) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{}||\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH3}
\end{array}\]
(iv) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CHO}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
\end{array}\]
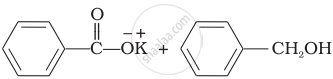
Treatment of compound \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.....}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{.....}||\\
\ce{Ph - O - C - Ph}
\end{array}\] with \[\ce{NaOH}\] solution yields
(i) Phenol
(ii) Sodium phenoxide
(iii) Sodium benzoate
(iv) Benzophenone
Which of the following conversions can be carried out by Clemmensen Reduction?
(i) Benzaldehyde into benzyl alcohol
(ii) Cyclohexanone into cyclohexane
(iii) Benzoyl chloride into benzaldehyde
(iv) Benzophenone into diphenyl methane
Through which of the following reactions number of carbon atoms can be increased in the chain?
(i) Grignard reaction
(ii) Cannizaro’s reaction
(iii) Aldol condensation
(iv) HVZ reaction
Benzophenone can be obtained by:
(i) Benzoyl chloride + Benzene + \[\ce{AlCl3}\]
(ii) Benzoyl chloride + Diphenyl cadmium
(iii) Benzoyl chloride + Phenyl magnesium chloride
(iv) Benzene + Carbon monoxide + \[\ce{ZnCl2}\]
Which of the following is the correct representation for intermediate of nucleophilic addition reaction to the given carbonyl compound (A):

(i) 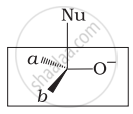
(ii) 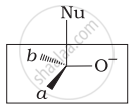
(iii) 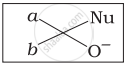
(iv) 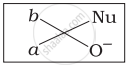
Why is there a large difference in the boiling points of butanal and butan-1-ol?
Write a test to differentiate between pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
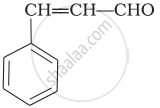
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
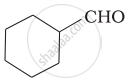
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - C - CH2 - CHO}\\
||\phantom{.}\\
\ce{O}\phantom{.}
\end{array}\]
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
\[\ce{CH3 - CH = CH - CHO}\]
Give the structure of the following compounds.
4-Nitropropiophenone
Give the structure of the following compounds.
2-Hydroxycyclopentanecarbaldehyde
Give the structure of the following compounds.
Phenyl acetaldehyde
Write IUPAC names of the following structures.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CHO}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CHO}\\
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC names of the following structures.
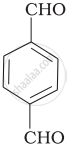
Write IUPAC names of the following structures.
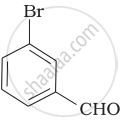
Benzaldehyde can be obtained from benzal chloride. Write reactions for obtaining benzalchloride and then benzaldehyde from it.
Name the electrophile produced in the reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous \[\ce{AlCl3}\]. Name the reaction also.
Oxidation of ketones involves carbon-carbon bond cleavage. Name the products formed on oxidation of 2, 5-dimethylhexan-3-one.
Arrange the following in decreasing order of their acidic strength and give reason for your answer.
\[\ce{CH3CH2OH, CH3COOH, ClCH2COOH, FCH2COOH, C6H5CH2COOH}\]
What product will be formed on reaction of propanal with 2-methylpropanal in the presence of \[\ce{NaOH}\]? What products will be formed? Write the name of the reaction also.
Compound ‘A’ was prepared by oxidation of compound ‘B’ with alkaline \[\ce{KMnO4}\]. Compound ‘A’ on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride gets converted back to compound ‘B’. When compound ‘A’ is heated with compound B in the presence of \[\ce{H2SO4}\] it produces fruity smell of compound C to which family the compounds ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ belong to?
Arrange the following in decreasing order of their acidic strength. Give explanation for the arrangement.
\[\ce{C6H5COOH, FCH2COOH, NO2CH2COOH}\]
Alkenes 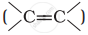 and carbonyl compounds
and carbonyl compounds 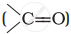 , both contain a π bond but alkenes show electrophilic addition reactions whereas carbonyl compounds show nucleophilic addition reactions. Explain.
, both contain a π bond but alkenes show electrophilic addition reactions whereas carbonyl compounds show nucleophilic addition reactions. Explain.
Carboxylic acids contain carbonyl group but do not show the nucleophilic addition reaction like aldehydes or ketones. Why?
Identify the compounds A, B and C in the following reaction.
\[\ce{CH3 - Br ->[Mg/ether] (A) ->[(i) CO][(ii) Water] (B) ->[CH3OH/H+][Δ] (C)}\]
Why are carboxylic acids more acidic than alcohols or phenols although all of them have hydrogen atom attached to a oxygen atom \[\ce{(-O-H)}\]?
Complete the following reaction sequence.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{O}\phantom{...............................................}\\
||\phantom{...............................................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH3 ->[(i) CH3MgBr][H2O] (A) ->[Na metal][Ether] (B) ->[CH3 - Br] (C)}
\end{array}\]
Ethylbenzene is generally prepared by acetylation of benzene followed by reduction and not by direct alkylation. Think of a possible reason.
Can Gatterman-Koch reaction be considered similar to Friedel Craft’s acylation? Discuss.
Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Common names) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Cinnamaldehyde | (a) | Pentanal |
| (ii) | Acetophenone | (b) | Prop-2-enal |
| (iii) | Valeraldehyde | (c) | 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one |
| (iv) | Acrolein | (d) | 3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
| (v) | Mesityl oxide | (e) | 1-Phenylethanone |
Match the acids given in Column I with their correct IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Acids) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Phthalic acid | (a) | Hexane-1,6-dioic acid |
| (ii) | Oxalic acid | (b) | Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid |
| (iii) | Succinic acid | (c) | Pentane-1,5-dioic acid |
| (iv) | Adipic acid | (d) | Butane-1,4-dioic acid |
| (v) | Glutaric acid | (e) | Ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
Match the reactions given in Column I with the suitable reagents given in Column II.
| Column I (Reactions) |
Column II (Reagents) |
| (i) Benzophenone Diphenylmethane | (a) \[\ce{LiAlH4}\] |
| (ii) Benzaldehyde 1-Phenylethanol | (b) \[\ce{DIBAL-H}\] |
| (iii) Cyclohexanone Cyclohexanol | (c) \[\ce{Zn(Hg)/Conc. HCl}\] |
| (iv) Phenyl benzoate Benzaldehyde | (d) \[\ce{CH3MgBr}\] |
Match the example given in Column I with the name of the reaction in Column II.
| Column I (Example) |
Column II (Reaction) |
||
| (i) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{...}\ce{O}\phantom{..............................}\ce{O}\phantom{}\\ \phantom{...}||\phantom{..............................}||\phantom{}\\ \ce{CH3 - C - Cl + H2 ->[Pd - C/BasO4] CH3 - C - H} \end{array}\] |
(a) | Friedel Crafts acylation |
| (ii) | 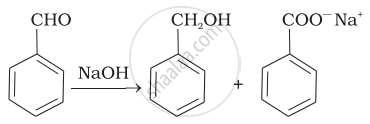 |
(b) | HVZ reaction |
| (iii) | 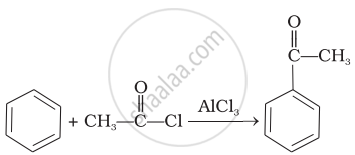 |
(c) | Aldol condensation |
| (iv) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{R - CH2 - COOH ->[Br/Red P] R - CH - COOH}\\ \phantom{.....................}|\\ \phantom{.......................}\ce{Br} \end{array}\] |
(d) | Cannizaro’s reaction |
| (v) | \[\ce{CH3 - CN ->[(i) SnCl2/HCl][(ii) H2O/H+] CH3CHO}\] | (e) | Rosenmund’s reductio |
| (vi) | \[\ce{2CH3CHO ->[NaOH] CH3 - CH = CHCHO}\] | (f) | Stephen’s reaction |
Assertion: Formaldehyde is a planar molecule.
Reason: It contains sp2 hybridised carbon atom.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reasson is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: Compounds containing \[\ce{-CHO}\] group are easily oxidised to corresponding carboxylic acids.
Reason: Carboxylic acids can be reduced to alcohols by treatment with \[\ce{LiAlH4}\].
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reasson is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: The α-hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is less acidic.
Reason: The anion formed after the loss of α-hydrogen atom is resonance stabilised.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reasson is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: Aromatic aldehydes and formaldehyde undergo Cannizaro reaction.
Reason: Aromatic aldehydes are almost as reactive as formaldehyde.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reasson is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: Aldehydes and ketones, both react with Tollen’s reagent to form silver mirror.
Reason: Both, aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reasson is not correct explanation of assertion.
An alkene ‘A’ (Mol. formula \[\ce{C5H10}\]) on ozonolysis gives a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and also forms iodoform on treatment with \[\ce{I2}\] and \[\ce{NaOH}\]. Compound ‘C’ does not give Fehling’s test but forms iodoform. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Write the reaction for ozonolysis and formation of iodoform from B and C.
An aromatic compound ‘A’ (Molecular formula \[\ce{C8H8O}\]) gives positive 2, 4-DNP test. It gives a yellow precipitate of compound ‘B’ on treatment with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution. Compound ‘A’ does not give Tollen’s or Fehling’s test. On drastic oxidation with potassium permanganate it forms a carboxylic acid ‘C’ (Molecular formula \[\ce{C7H6O2}\]), which is also formed along with the yellow compound in the above reaction. Identify A, B and C and write all the reactions involved.
Write down functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula \[\ce{C3H6O}\]. Which isomer will react faster with \[\ce{HCN}\] and why? Explain the mechanism of the reaction also. Will the reaction lead to the completion with the conversion of whole reactant into product at reaction conditions? If a strong acid is added to the reaction mixture what will be the effect on concentration of the product and why?
When liquid ‘A’ is treated with a freshly prepared ammoniacal silver nitrate solution, it gives bright silver mirror. The liquid forms a white crystalline solid on treatment with sodium hydrogensulphite. Liquid ‘B’ also forms a white crystalline solid with sodium hydrogensulphite but it does not give test with ammoniacal silver nitrate. Which of the two liquids is aldehyde? Write the chemical equations of these reactions also.
Solutions for 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE 12 (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids are Introduction of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids, Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones, Nature of Carbonyl Group, Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones, Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Addition Reactions, Uses of Aldehydes and Ketones, Introduction of Carboxylic Acids, Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids, Structure of the Carboxyl group, Methods of Preparation of Carboxylic Acids, Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids, Uses of Carboxylic Acids, Preparation of Aldehydes, Preparation of Ketones, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Reduction, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Oxidation, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Reactions Due to α-hydrogen, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Other Reactions, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving Cleavege of O-H Bond, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving Cleavege of C-OH Bond, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving –COOH Group, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Substitution Reactions in the Hydrocarbon Part, Structure of the Carbonyl Group.
Using NCERT Exemplar Chemistry [English] Class 12 solutions Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Chemistry [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 12, Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Chemistry [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.