Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Common names) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Cinnamaldehyde | (a) | Pentanal |
| (ii) | Acetophenone | (b) | Prop-2-enal |
| (iii) | Valeraldehyde | (c) | 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one |
| (iv) | Acrolein | (d) | 3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
| (v) | Mesityl oxide | (e) | 1-Phenylethanone |
Solution
| Column I (Common names) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Cinnamaldehyde | (d) | 3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
| (ii) | Acetophenone | (e) | 1-Phenylethanone |
| (iii) | Valeraldehyde | (a) | Pentanal |
| (iv) | Acrolein | (b) | Prop-2-enal |
| (v) | Mesityl oxide | (c) | 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one |
Explanation:
| (Common names) | Structure | (IUPAC names) |
| (i) Cinnamaldehyde | 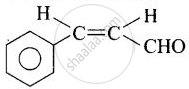 |
3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
| (ii) Acetophenone | 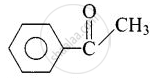 |
1-Phenylethanone |
| (iii) Valeraldehyde | 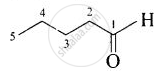 |
Pentanal |
| (iv) Acrolein | 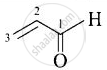 |
Prop-2-enal |
| (v) Mesityl oxide | 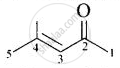 |
4-Methylpent-3-en-2- one |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the product in the following reaction
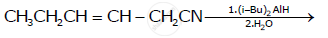
Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions : Rosenmund reduction
Esters react with DIBAL-H to produce:
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage to give benzaldehyde. The reagent used for the purpose is one of the following.
Match the example given in Column I with the name of the reaction in Column II.
| Column I (Example) |
Column II (Reaction) |
||
| (i) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{...}\ce{O}\phantom{..............................}\ce{O}\phantom{}\\ \phantom{...}||\phantom{..............................}||\phantom{}\\ \ce{CH3 - C - Cl + H2 ->[Pd - C/BasO4] CH3 - C - H} \end{array}\] |
(a) | Friedel Crafts acylation |
| (ii) | 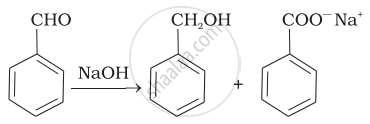 |
(b) | HVZ reaction |
| (iii) | 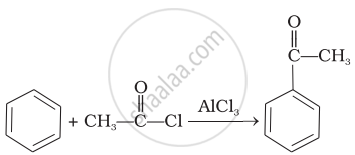 |
(c) | Aldol condensation |
| (iv) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{R - CH2 - COOH ->[Br/Red P] R - CH - COOH}\\ \phantom{.....................}|\\ \phantom{.......................}\ce{Br} \end{array}\] |
(d) | Cannizaro’s reaction |
| (v) | \[\ce{CH3 - CN ->[(i) SnCl2/HCl][(ii) H2O/H+] CH3CHO}\] | (e) | Rosenmund’s reductio |
| (vi) | \[\ce{2CH3CHO ->[NaOH] CH3 - CH = CHCHO}\] | (f) | Stephen’s reaction |
An alkene ‘A’ (Mol. formula \[\ce{C5H10}\]) on ozonolysis gives a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and also forms iodoform on treatment with \[\ce{I2}\] and \[\ce{NaOH}\]. Compound ‘C’ does not give Fehling’s test but forms iodoform. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Write the reaction for ozonolysis and formation of iodoform from B and C.
The strongest base among the following
Aldehydes are the first oxidation products of ______.
Convert the following:
Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
An organic compound with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H7NO2}\] exists in three isomeric forms, the isomer ‘A’ has the highest melting point of the three. ‘A’ on reduction gives compound ‘B’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H9N}\]. ‘B’ on treatment with \[\ce{NaNO2/HCl}\] at 0-5° C to form compound ‘C’. On treating C with \[\ce{H3PO2}\], it gets converted to D with formula \[\ce{C7H8}\], which on further reaction with \[\ce{CrO2Cl2}\] followed by hydrolysis forms ‘E’ \[\ce{C7H6O}\]. Write the structure of compounds A to E. Write the chemical equations involved.
