Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Match the example given in Column I with the name of the reaction in Column II.
| Column I (Example) |
Column II (Reaction) |
||
| (i) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{...}\ce{O}\phantom{..............................}\ce{O}\phantom{}\\ \phantom{...}||\phantom{..............................}||\phantom{}\\ \ce{CH3 - C - Cl + H2 ->[Pd - C/BasO4] CH3 - C - H} \end{array}\] |
(a) | Friedel Crafts acylation |
| (ii) | 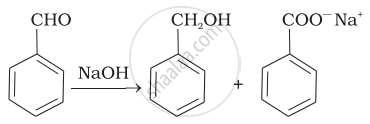 |
(b) | HVZ reaction |
| (iii) | 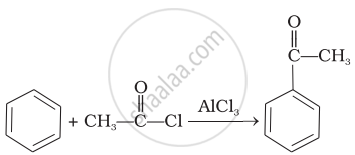 |
(c) | Aldol condensation |
| (iv) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{R - CH2 - COOH ->[Br/Red P] R - CH - COOH}\\ \phantom{.....................}|\\ \phantom{.......................}\ce{Br} \end{array}\] |
(d) | Cannizaro’s reaction |
| (v) | \[\ce{CH3 - CN ->[(i) SnCl2/HCl][(ii) H2O/H+] CH3CHO}\] | (e) | Rosenmund’s reductio |
| (vi) | \[\ce{2CH3CHO ->[NaOH] CH3 - CH = CHCHO}\] | (f) | Stephen’s reaction |
Solution
| Column I (Example) |
Column II (Reaction) |
||
| (i) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{...}\ce{O}\phantom{..............................}\ce{O}\phantom{}\\ \phantom{...}||\phantom{..............................}||\phantom{}\\ \ce{CH3 - C - Cl + H2 ->[Pd - C/BasO4] CH3 - C - H} \end{array}\] |
(e) | Rosenmund’s reductio |
| (ii) |  |
(d) | Cannizaro’s reaction |
| (iii) |  |
(a) | Friedel Crafts acylation |
| (iv) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{R - CH2 - COOH ->[Br/Red P] R - CH - COOH}\\ \phantom{.....................}|\\ \phantom{.......................}\ce{Br} \end{array}\] |
(b) | HVZ reaction |
| (v) | \[\ce{CH3 - CN ->[(i) SnCl2/HCl][(ii) H2O/H+] CH3CHO}\] | (f) | Stephen’s reaction |
| (vi) | \[\ce{2CH3CHO ->[NaOH] CH3 - CH = CHCHO}\] | (c) | Aldol condensation |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the product in the following reaction:
When 0.4g of oxalic acid is dissolved in 40g of benzene, the freezing point of the solution is lowered by 0.45 K. Calculate the degree of association of acetic acid. Acetic acid forms dimer when dissolved in benzene.
(Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol-1, at. wt. C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
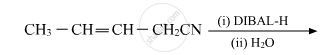
Aldehydes are produced on reduction of the following by DIBAL-H:
Ethylbenzene is generally prepared by acetylation of benzene followed by reduction and not by direct alkylation. Think of a possible reason.
What is the name of the given reaction of preparation of aldehyde?
\[\ce{C3COCl ->[H2][Pd/BaSO4] CH3CHO + HCl}\]
When 2 – hydroxyl benzoic acid distilled with zinc dust, it give
The reagent in friedel - craft reaction is:
Convert the following:
Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
Account for the following:
N-ethylbenzene sulphonyl amide is soluble in alkali.
Write the name of the reaction, structure and IUPAC name of the product formed when:
CH3CH2CN reacts with stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid, followed by hydrolysis.
