Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Common names) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Cinnamaldehyde | (a) | Pentanal |
| (ii) | Acetophenone | (b) | Prop-2-enal |
| (iii) | Valeraldehyde | (c) | 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one |
| (iv) | Acrolein | (d) | 3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
| (v) | Mesityl oxide | (e) | 1-Phenylethanone |
उत्तर
| Column I (Common names) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Cinnamaldehyde | (d) | 3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
| (ii) | Acetophenone | (e) | 1-Phenylethanone |
| (iii) | Valeraldehyde | (a) | Pentanal |
| (iv) | Acrolein | (b) | Prop-2-enal |
| (v) | Mesityl oxide | (c) | 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one |
Explanation:
| (Common names) | Structure | (IUPAC names) |
| (i) Cinnamaldehyde | 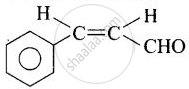 |
3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
| (ii) Acetophenone | 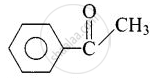 |
1-Phenylethanone |
| (iii) Valeraldehyde | 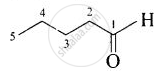 |
Pentanal |
| (iv) Acrolein | 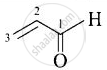 |
Prop-2-enal |
| (v) Mesityl oxide | 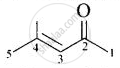 |
4-Methylpent-3-en-2- one |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
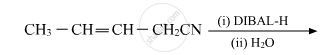
Write the product in the following reaction:
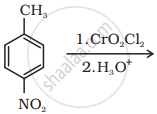
Write the structure of the product of the following reaction:
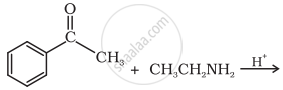
Predict the product of the following reaction:
Ozonolysis of alkenes followed by the reaction with zinc dust and water gives ____________ depending on the substitution pattern of the alkene.
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be done using which of the following reagents.
An alkene ‘A’ (Mol. formula \[\ce{C5H10}\]) on ozonolysis gives a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and also forms iodoform on treatment with \[\ce{I2}\] and \[\ce{NaOH}\]. Compound ‘C’ does not give Fehling’s test but forms iodoform. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Write the reaction for ozonolysis and formation of iodoform from B and C.
What is the name of the given reaction of preparation of aldehyde?
\[\ce{C3COCl ->[H2][Pd/BaSO4] CH3CHO + HCl}\]
The general formula CnH2NO2 could be for open chain
An organic compound with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H7NO2}\] exists in three isomeric forms, the isomer ‘A’ has the highest melting point of the three. ‘A’ on reduction gives compound ‘B’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H9N}\]. ‘B’ on treatment with \[\ce{NaNO2/HCl}\] at 0-5° C to form compound ‘C’. On treating C with \[\ce{H3PO2}\], it gets converted to D with formula \[\ce{C7H8}\], which on further reaction with \[\ce{CrO2Cl2}\] followed by hydrolysis forms ‘E’ \[\ce{C7H6O}\]. Write the structure of compounds A to E. Write the chemical equations involved.
Write the name of the reaction, structure and IUPAC name of the product formed when:
CH3CH2CN reacts with stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid, followed by hydrolysis.
