Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the structure of the product of the following reaction:
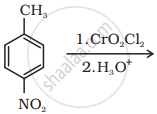
उत्तर
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
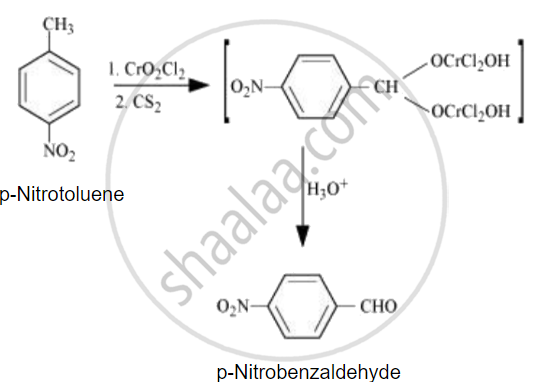
Predict the product of the following reaction:
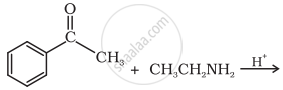
Write the reaction involved in the Stephen reduction
When 0.4g of oxalic acid is dissolved in 40g of benzene, the freezing point of the solution is lowered by 0.45 K. Calculate the degree of association of acetic acid. Acetic acid forms dimer when dissolved in benzene.
(Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol-1, at. wt. C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be stopped at the aldehyde stage to give benzaldehyde. The reagent used for the purpose is one of the following.
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be done using which of the following reagents.
Name the electrophile produced in the reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous \[\ce{AlCl3}\]. Name the reaction also.
Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Common names) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Cinnamaldehyde | (a) | Pentanal |
| (ii) | Acetophenone | (b) | Prop-2-enal |
| (iii) | Valeraldehyde | (c) | 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one |
| (iv) | Acrolein | (d) | 3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
| (v) | Mesityl oxide | (e) | 1-Phenylethanone |
Match the acids given in Column I with their correct IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Acids) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Phthalic acid | (a) | Hexane-1,6-dioic acid |
| (ii) | Oxalic acid | (b) | Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid |
| (iii) | Succinic acid | (c) | Pentane-1,5-dioic acid |
| (iv) | Adipic acid | (d) | Butane-1,4-dioic acid |
| (v) | Glutaric acid | (e) | Ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
Match the example given in Column I with the name of the reaction in Column II.
| Column I (Example) |
Column II (Reaction) |
||
| (i) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{...}\ce{O}\phantom{..............................}\ce{O}\phantom{}\\ \phantom{...}||\phantom{..............................}||\phantom{}\\ \ce{CH3 - C - Cl + H2 ->[Pd - C/BasO4] CH3 - C - H} \end{array}\] |
(a) | Friedel Crafts acylation |
| (ii) | 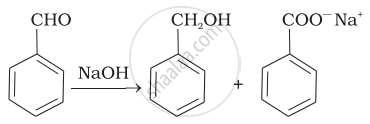 |
(b) | HVZ reaction |
| (iii) | 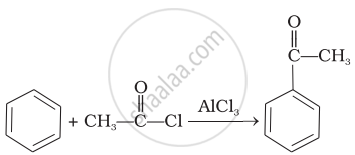 |
(c) | Aldol condensation |
| (iv) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{R - CH2 - COOH ->[Br/Red P] R - CH - COOH}\\ \phantom{.....................}|\\ \phantom{.......................}\ce{Br} \end{array}\] |
(d) | Cannizaro’s reaction |
| (v) | \[\ce{CH3 - CN ->[(i) SnCl2/HCl][(ii) H2O/H+] CH3CHO}\] | (e) | Rosenmund’s reductio |
| (vi) | \[\ce{2CH3CHO ->[NaOH] CH3 - CH = CHCHO}\] | (f) | Stephen’s reaction |
What is the name of the given reaction of preparation of aldehyde?
\[\ce{C3COCl ->[H2][Pd/BaSO4] CH3CHO + HCl}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\phantom{......}\ce{Cl}
\end{array}\] obtained by chlorination of n-butane, will be
The reaction

Benz aldehyde + NaOH →
The general formula CnH2NO2 could be for open chain
The reagent in friedel - craft reaction is:
Predict the reagent for carrying out the following transformations:
Benzoyl chloride to Benzaldehyde
Account for the following:
N-ethylbenzene sulphonyl amide is soluble in alkali.
Account for the following:
Reduction of nitrobenzene using Fe and HCl is preferred over Sn and HCl.
