Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
When 0.4g of oxalic acid is dissolved in 40g of benzene, the freezing point of the solution is lowered by 0.45 K. Calculate the degree of association of acetic acid. Acetic acid forms dimer when dissolved in benzene.
(Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol-1, at. wt. C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
उत्तर
∆Tf = 0.45 K
i = ?
Kf = 5.12 K kg mol-1
MB of CH3COOH = 60
WA = 40 g
WB = 0.4 g
We know that
`triangle "T"_"f" = "i""K"_"f" . "W"_"B"/"M"_"B" xx 1000/"W"_"A"`
`0.45 = "i" xx 5.12 xx 0.4/60 xx 1000/40`
i = `(0.45 xx 60 xx 40)/(0.4 xx 1000 xx 5.12)`
`= (45 xx 60 xx 40)/(40 xx 1000 xx 5.12)`
`= 2700/5120 = 135/256 = 0.5273`
Let degree of association of acetic acid = α
∴ α = `("i" - 1)/(1/"n" - 1)` For CH3COOH , n = 2
`= (0.5273-1)/(1/2 -1) = 0.4727/0.5000 = 0.9514`
∴ Degree of association of acetic acid (α) = 0.9514 or 95.14%
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Predict the product of the following reaction:
Ozonolysis of alkenes followed by the reaction with zinc dust and water gives ____________ depending on the substitution pattern of the alkene.
Ethylbenzene is generally prepared by acetylation of benzene followed by reduction and not by direct alkylation. Think of a possible reason.
An alkene ‘A’ (Mol. formula \[\ce{C5H10}\]) on ozonolysis gives a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and also forms iodoform on treatment with \[\ce{I2}\] and \[\ce{NaOH}\]. Compound ‘C’ does not give Fehling’s test but forms iodoform. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Write the reaction for ozonolysis and formation of iodoform from B and C.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\phantom{......}\ce{Cl}
\end{array}\] obtained by chlorination of n-butane, will be
The reaction

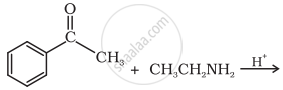
The intermediate compound ‘X’ in the following chemical reaction is:
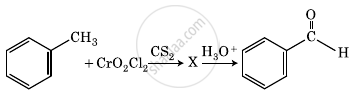
Convert the following:
Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
Explain the following reactions:
Stephan reaction
Account for the following:
N-ethylbenzene sulphonyl amide is soluble in alkali.
