Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the acids given in Column I with their correct IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Acids) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Phthalic acid | (a) | Hexane-1,6-dioic acid |
| (ii) | Oxalic acid | (b) | Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid |
| (iii) | Succinic acid | (c) | Pentane-1,5-dioic acid |
| (iv) | Adipic acid | (d) | Butane-1,4-dioic acid |
| (v) | Glutaric acid | (e) | Ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
उत्तर
| Column I (Acids) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Phthalic acid | (b) | Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid |
| (ii) | Oxalic acid | (e) | Ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
| (iii) | Succinic acid | (d) | Butane-1,4-dioic acid |
| (iv) | Adipic acid | (a) | Hexane-1,6-dioic acid |
| (v) | Glutaric acid | (c) | Pentane-1,5-dioic acid |
Explanation:
| Acids | IUPAC names | Structure |
| (i) Phthalic acid | Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid | 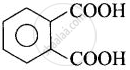 |
| (ii) Oxalic acid | Ethane-1,2-dioic acid | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{COOH}\\ |\phantom{......}\\ \ce{COOH} \end{array}\] |
| (iii) Succinic acid | Butane-1,4-dioic acid | 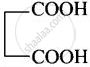 |
| (iv) Adipic acid | Hexane-1,6-dioic acid | 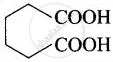 |
| (v) Glutaric acid | Pentane-1,5-dioic acid | 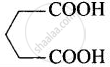 |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the product in the following reaction:
Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions : Rosenmund reduction
Write the structure of the product of the following reaction:
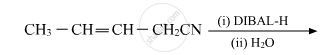
Aldehydes are produced on reduction of the following by DIBAL-H:
Match the example given in Column I with the name of the reaction in Column II.
| Column I (Example) |
Column II (Reaction) |
||
| (i) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{...}\ce{O}\phantom{..............................}\ce{O}\phantom{}\\ \phantom{...}||\phantom{..............................}||\phantom{}\\ \ce{CH3 - C - Cl + H2 ->[Pd - C/BasO4] CH3 - C - H} \end{array}\] |
(a) | Friedel Crafts acylation |
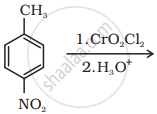
| (ii) | 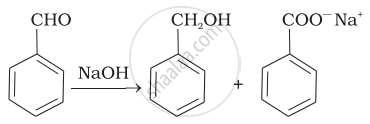 |
(b) | HVZ reaction |
| (iii) | 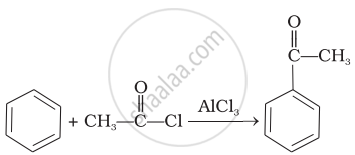 |
(c) | Aldol condensation |
| (iv) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{R - CH2 - COOH ->[Br/Red P] R - CH - COOH}\\ \phantom{.....................}|\\ \phantom{.......................}\ce{Br} \end{array}\] |
(d) | Cannizaro’s reaction |
| (v) | \[\ce{CH3 - CN ->[(i) SnCl2/HCl][(ii) H2O/H+] CH3CHO}\] | (e) | Rosenmund’s reductio |
| (vi) | \[\ce{2CH3CHO ->[NaOH] CH3 - CH = CHCHO}\] | (f) | Stephen’s reaction |
In the chromyl chloride test, the final step results in the formation of a yellow precipitate of the following:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\phantom{......}\ce{Cl}
\end{array}\] obtained by chlorination of n-butane, will be
Benz aldehyde + NaOH →
The number of chiral carbon in glucose is:-
Assertion (A): Strong oxidising agents oxidise toluene and its derivatives to benzoic acids.
Reason (R): It is possible to stop the oxidation of toluene at the aldehyde stage with suitable reagents.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
