Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions : Rosenmund reduction
Give balanced equations for the following name reactions
Rosenmund reaction
उत्तर १

उत्तर २
Rosemund reaction:
उत्तर ३
Rosemund reaction:

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
p-Nitrobenzaldehyde
Write the reaction involved in the Stephen reduction
When 0.4g of oxalic acid is dissolved in 40g of benzene, the freezing point of the solution is lowered by 0.45 K. Calculate the degree of association of acetic acid. Acetic acid forms dimer when dissolved in benzene.
(Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol-1, at. wt. C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
Ozonolysis of alkenes followed by the reaction with zinc dust and water gives ____________ depending on the substitution pattern of the alkene.
Aldehydes are produced on reduction of the following by DIBAL-H:
Name the electrophile produced in the reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous \[\ce{AlCl3}\]. Name the reaction also.
Match the acids given in Column I with their correct IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Acids) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Phthalic acid | (a) | Hexane-1,6-dioic acid |
| (ii) | Oxalic acid | (b) | Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid |
| (iii) | Succinic acid | (c) | Pentane-1,5-dioic acid |
| (iv) | Adipic acid | (d) | Butane-1,4-dioic acid |
| (v) | Glutaric acid | (e) | Ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
An aromatic compound ‘A’ (Molecular formula \[\ce{C8H8O}\]) gives positive 2, 4-DNP test. It gives a yellow precipitate of compound ‘B’ on treatment with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution. Compound ‘A’ does not give Tollen’s or Fehling’s test. On drastic oxidation with potassium permanganate it forms a carboxylic acid ‘C’ (Molecular formula \[\ce{C7H6O2}\]), which is also formed along with the yellow compound in the above reaction. Identify A, B and C and write all the reactions involved.
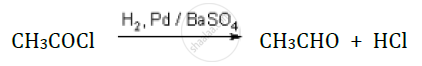
What is the name of the given reaction of preparation of aldehyde?
\[\ce{C3COCl ->[H2][Pd/BaSO4] CH3CHO + HCl}\]
When 2 – hydroxyl benzoic acid distilled with zinc dust, it give
The reagent in friedel - craft reaction is:
Explain the following reactions:
Stephan reaction
Predict the reagent for carrying out the following transformations:
Benzoyl chloride to Benzaldehyde
The reaction of benzene with CO and HCl in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 gives ______.
An organic compound with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H7NO2}\] exists in three isomeric forms, the isomer ‘A’ has the highest melting point of the three. ‘A’ on reduction gives compound ‘B’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H9N}\]. ‘B’ on treatment with \[\ce{NaNO2/HCl}\] at 0-5° C to form compound ‘C’. On treating C with \[\ce{H3PO2}\], it gets converted to D with formula \[\ce{C7H8}\], which on further reaction with \[\ce{CrO2Cl2}\] followed by hydrolysis forms ‘E’ \[\ce{C7H6O}\]. Write the structure of compounds A to E. Write the chemical equations involved.
Write the name of the reaction, structure and IUPAC name of the product formed when:
CH3CH2CN reacts with stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid, followed by hydrolysis.
