Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An aromatic compound ‘A’ (Molecular formula \[\ce{C8H8O}\]) gives positive 2, 4-DNP test. It gives a yellow precipitate of compound ‘B’ on treatment with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution. Compound ‘A’ does not give Tollen’s or Fehling’s test. On drastic oxidation with potassium permanganate it forms a carboxylic acid ‘C’ (Molecular formula \[\ce{C7H6O2}\]), which is also formed along with the yellow compound in the above reaction. Identify A, B and C and write all the reactions involved.
उत्तर
Molecular formula of compound is \[\ce{C8HgO}\]. As ‘A’ does not give Tollens’ or Fehling’s test. It must be a ketone. It gives positive test with 2, 4-DNP and iodoform test. It means it is methyl ketone.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the product in the following reaction:
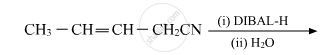
Write the structure of the product of the following reaction:
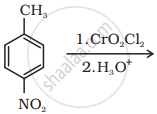
Write the reaction involved in the Stephen reduction
Esters react with DIBAL-H to produce:
Aldehydes are prepared by reducing nitriles to corresponding imines with stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid. This reaction is called:
Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Common names) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Cinnamaldehyde | (a) | Pentanal |
| (ii) | Acetophenone | (b) | Prop-2-enal |
| (iii) | Valeraldehyde | (c) | 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one |
| (iv) | Acrolein | (d) | 3-Phenylprop-2-enal |
| (v) | Mesityl oxide | (e) | 1-Phenylethanone |
Match the acids given in Column I with their correct IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Acids) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Phthalic acid | (a) | Hexane-1,6-dioic acid |
| (ii) | Oxalic acid | (b) | Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid |
| (iii) | Succinic acid | (c) | Pentane-1,5-dioic acid |
| (iv) | Adipic acid | (d) | Butane-1,4-dioic acid |
| (v) | Glutaric acid | (e) | Ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
Match the example given in Column I with the name of the reaction in Column II.
| Column I (Example) |
Column II (Reaction) |
||
| (i) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{...}\ce{O}\phantom{..............................}\ce{O}\phantom{}\\ \phantom{...}||\phantom{..............................}||\phantom{}\\ \ce{CH3 - C - Cl + H2 ->[Pd - C/BasO4] CH3 - C - H} \end{array}\] |
(a) | Friedel Crafts acylation |
| (ii) | 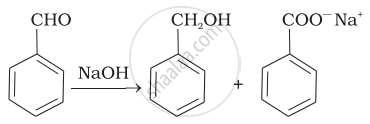 |
(b) | HVZ reaction |
| (iii) | 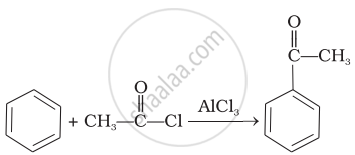 |
(c) | Aldol condensation |
| (iv) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{R - CH2 - COOH ->[Br/Red P] R - CH - COOH}\\ \phantom{.....................}|\\ \phantom{.......................}\ce{Br} \end{array}\] |
(d) | Cannizaro’s reaction |
| (v) | \[\ce{CH3 - CN ->[(i) SnCl2/HCl][(ii) H2O/H+] CH3CHO}\] | (e) | Rosenmund’s reductio |
| (vi) | \[\ce{2CH3CHO ->[NaOH] CH3 - CH = CHCHO}\] | (f) | Stephen’s reaction |
The general formula CnH2NO2 could be for open chain
Aldehydes are the first oxidation products of ______.
