Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An aromatic compound ‘A’ (Molecular formula \[\ce{C8H8O}\]) gives positive 2, 4-DNP test. It gives a yellow precipitate of compound ‘B’ on treatment with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution. Compound ‘A’ does not give Tollen’s or Fehling’s test. On drastic oxidation with potassium permanganate it forms a carboxylic acid ‘C’ (Molecular formula \[\ce{C7H6O2}\]), which is also formed along with the yellow compound in the above reaction. Identify A, B and C and write all the reactions involved.
उत्तर
Molecular formula of compound is \[\ce{C8HgO}\]. As ‘A’ does not give Tollens’ or Fehling’s test. It must be a ketone. It gives positive test with 2, 4-DNP and iodoform test. It means it is methyl ketone.

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
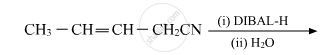
Write the product in the following reaction:
When 0.4g of oxalic acid is dissolved in 40g of benzene, the freezing point of the solution is lowered by 0.45 K. Calculate the degree of association of acetic acid. Acetic acid forms dimer when dissolved in benzene.
(Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol-1, at. wt. C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
Ethylbenzene is generally prepared by acetylation of benzene followed by reduction and not by direct alkylation. Think of a possible reason.
Match the acids given in Column I with their correct IUPAC names given in Column II.
| Column I (Acids) |
Column II (IUPAC names) |
||
| (i) | Phthalic acid | (a) | Hexane-1,6-dioic acid |
| (ii) | Oxalic acid | (b) | Benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid |
| (iii) | Succinic acid | (c) | Pentane-1,5-dioic acid |
| (iv) | Adipic acid | (d) | Butane-1,4-dioic acid |
| (v) | Glutaric acid | (e) | Ethane-1,2-dioic acid |
An alkene ‘A’ (Mol. formula \[\ce{C5H10}\]) on ozonolysis gives a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and also forms iodoform on treatment with \[\ce{I2}\] and \[\ce{NaOH}\]. Compound ‘C’ does not give Fehling’s test but forms iodoform. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Write the reaction for ozonolysis and formation of iodoform from B and C.
In the chromyl chloride test, the final step results in the formation of a yellow precipitate of the following:
Assertion (A): Strong oxidising agents oxidise toluene and its derivatives to benzoic acids.
Reason (R): It is possible to stop the oxidation of toluene at the aldehyde stage with suitable reagents.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Account for the following:
N-ethylbenzene sulphonyl amide is soluble in alkali.
Account for the following:
Reduction of nitrobenzene using Fe and HCl is preferred over Sn and HCl.
Write the name of the reaction, structure and IUPAC name of the product formed when:
CH3CH2CN reacts with stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid, followed by hydrolysis.
