Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Compound ‘A’ was prepared by oxidation of compound ‘B’ with alkaline \[\ce{KMnO4}\]. Compound ‘A’ on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride gets converted back to compound ‘B’. When compound ‘A’ is heated with compound B in the presence of \[\ce{H2SO4}\] it produces fruity smell of compound C to which family the compounds ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ belong to?
Solution
When alkaline \[\ce{KMnO4}\] oxidises compound ‘B’ with compound ‘A’, acid is formed.
\[\ce{B ->[{[O]}][alkaline KMnO4] A -> acid}\]
When compound ‘A’ is reduced with \[\ce{LiAlH4}\], it transforms into compound ‘B’. The letter ‘B’ stands for a type of alcoholic beverage.
\[\ce{A ->[LiAlH4] B -> Alcohol}\]
When compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ are heated with conc. \[\ce{H2SO4}\], compound ‘C’ is formed which has a fruity odour.
\[\ce{A + B ->[A][H2SO4] fruitysmell (ester)}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A compound 'A' of molecular formula C2H3OCl undergoes a series of reactions as shown below. Write the structures of A, B, C and D in the following reactions :
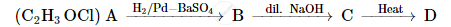
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Aldol
How will you convert ethanal into the following compound?
Butane-1, 3-diol
Write structural formulas and names of four possible aldol condensation products from propanal and butanal. In each case, indicate which aldehyde acts as nucleophile and which as electrophile.
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C6H5CHO}\phantom{............}\\
\phantom{........}\ce{+\phantom{......}\ce{->[dil.NaOH][\Delta]}}\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3CH2CHO}\phantom{............}
\end{array}\]
Give reasons Acetylation of aniline reduces its activation effect.
Write chemical equations of the following reaction :
Benzoyl chloride is hydrogenated in the presence of `"Pd"/(BaSO_4)`
Which of the following compounds do not undergo aldol condensation?
(i) \[\ce{CH3 - CHO}\]
(ii) 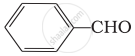
(iii) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{}||\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH3}
\end{array}\]
(iv) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CHO}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
\end{array}\]
Assertion: The α-hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is less acidic.
Reason: The anion formed after the loss of α-hydrogen atom is resonance stabilised.
Assertion (A): The final product in Aldol condensation is always α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
Reason (R): α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds are stabilised due to conjugation.
