Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Compound ‘A’ was prepared by oxidation of compound ‘B’ with alkaline \[\ce{KMnO4}\]. Compound ‘A’ on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride gets converted back to compound ‘B’. When compound ‘A’ is heated with compound B in the presence of \[\ce{H2SO4}\] it produces fruity smell of compound C to which family the compounds ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ belong to?
उत्तर
When alkaline \[\ce{KMnO4}\] oxidises compound ‘B’ with compound ‘A’, acid is formed.
\[\ce{B ->[{[O]}][alkaline KMnO4] A -> acid}\]
When compound ‘A’ is reduced with \[\ce{LiAlH4}\], it transforms into compound ‘B’. The letter ‘B’ stands for a type of alcoholic beverage.
\[\ce{A ->[LiAlH4] B -> Alcohol}\]
When compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ are heated with conc. \[\ce{H2SO4}\], compound ‘C’ is formed which has a fruity odour.
\[\ce{A + B ->[A][H2SO4] fruitysmell (ester)}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A compound 'A' of molecular formula C2H3OCl undergoes a series of reactions as shown below. Write the structures of A, B, C and D in the following reactions :
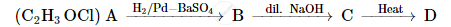
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C6H5CHO}\phantom{............}\\
\phantom{........}\ce{+\phantom{......}\ce{->[dil.NaOH][\Delta]}}\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3CH2CHO}\phantom{............}
\end{array}\]
Give reasons to support the answer:
Presence of Alpha hydrogen in aldehydes and ketones is essential for aldol condensation.
Which of the following gives aldol con~ensation reaction?
The major product of the following reaction is:
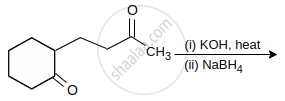
Which of the following does not give aldol condensation reaction?
Why is the α-hydrogens of aldehydes and ketones are acidic in nature?
Assertion (A): The final product in Aldol condensation is always α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
Reason (R): α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds are stabilised due to conjugation.

Identify A and B:
When acetaldehyde is treated with dilute NaOH, the following reaction is observed.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{2CH3 - CHO ->[dil.NaOH] CH3 - CH - CH2 - CHO}\\
\phantom{...............}|\\
\phantom{.................}\ce{OH}
\end{array}\]
- What are the functional groups in the product?
- Can another product be formed during the same reaction? (Deduce the answer by doing atomic audit of reactant and product).
- Is this an addition reaction or condensation reaction?
