Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Name the electrophile produced in the reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous \[\ce{AlCl3}\]. Name the reaction also.
Solution
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{O}\phantom{.......................}\ce{O}\phantom{...............................}\\
\phantom{}||\phantom{.......................}||\phantom{...............................}\\
\ce{C6HC - Cl + AlCl3 -> C6H5\overset{δ+}{C - Cl} = \overset{δ-}{Alcl3} -> C6H5Co+ + AlCl4}
\end{array}\]
Friedel–Crafts acylation reaction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
p-Nitrobenzaldehyde
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be done using which of the following reagents.
Match the example given in Column I with the name of the reaction in Column II.
| Column I (Example) |
Column II (Reaction) |
||
| (i) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{...}\ce{O}\phantom{..............................}\ce{O}\phantom{}\\ \phantom{...}||\phantom{..............................}||\phantom{}\\ \ce{CH3 - C - Cl + H2 ->[Pd - C/BasO4] CH3 - C - H} \end{array}\] |
(a) | Friedel Crafts acylation |
| (ii) | 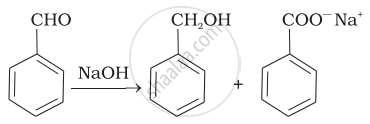 |
(b) | HVZ reaction |
| (iii) | 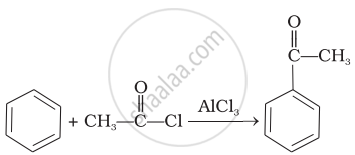 |
(c) | Aldol condensation |
| (iv) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{R - CH2 - COOH ->[Br/Red P] R - CH - COOH}\\ \phantom{.....................}|\\ \phantom{.......................}\ce{Br} \end{array}\] |
(d) | Cannizaro’s reaction |
| (v) | \[\ce{CH3 - CN ->[(i) SnCl2/HCl][(ii) H2O/H+] CH3CHO}\] | (e) | Rosenmund’s reductio |
| (vi) | \[\ce{2CH3CHO ->[NaOH] CH3 - CH = CHCHO}\] | (f) | Stephen’s reaction |
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\phantom{......}\ce{Cl}
\end{array}\] obtained by chlorination of n-butane, will be
The intermediate compound ‘X’ in the following chemical reaction is:
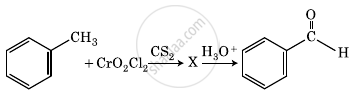
Convert the following:
Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
The reaction of benzene with CO and HCl in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 gives ______.
Assertion (A): Strong oxidising agents oxidise toluene and its derivatives to benzoic acids.
Reason (R): It is possible to stop the oxidation of toluene at the aldehyde stage with suitable reagents.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
An organic compound with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H7NO2}\] exists in three isomeric forms, the isomer ‘A’ has the highest melting point of the three. ‘A’ on reduction gives compound ‘B’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H9N}\]. ‘B’ on treatment with \[\ce{NaNO2/HCl}\] at 0-5° C to form compound ‘C’. On treating C with \[\ce{H3PO2}\], it gets converted to D with formula \[\ce{C7H8}\], which on further reaction with \[\ce{CrO2Cl2}\] followed by hydrolysis forms ‘E’ \[\ce{C7H6O}\]. Write the structure of compounds A to E. Write the chemical equations involved.
Account for the following:
N-ethylbenzene sulphonyl amide is soluble in alkali.
