Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Assertion (A): Strong oxidising agents oxidise toluene and its derivatives to benzoic acids.
Reason (R): It is possible to stop the oxidation of toluene at the aldehyde stage with suitable reagents.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Options
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Solution
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the chemical equations to illustrate the following name reactions : Rosenmund reduction
When 0.4g of oxalic acid is dissolved in 40g of benzene, the freezing point of the solution is lowered by 0.45 K. Calculate the degree of association of acetic acid. Acetic acid forms dimer when dissolved in benzene.
(Kf for benzene = 5.12 K kg mol-1, at. wt. C = 12, H = 1, O = 16)
The oxidation of toluene to benzoic acid can be done using which of the following reagents.
Name the electrophile produced in the reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous \[\ce{AlCl3}\]. Name the reaction also.
An alkene ‘A’ (Mol. formula \[\ce{C5H10}\]) on ozonolysis gives a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and also forms iodoform on treatment with \[\ce{I2}\] and \[\ce{NaOH}\]. Compound ‘C’ does not give Fehling’s test but forms iodoform. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Write the reaction for ozonolysis and formation of iodoform from B and C.
The reaction

Aldehydes are the first oxidation products of ______.
The reagent in friedel - craft reaction is:
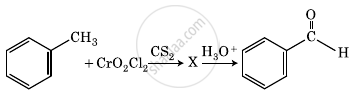
The intermediate compound ‘X’ in the following chemical reaction is:
An organic compound with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H7NO2}\] exists in three isomeric forms, the isomer ‘A’ has the highest melting point of the three. ‘A’ on reduction gives compound ‘B’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H9N}\]. ‘B’ on treatment with \[\ce{NaNO2/HCl}\] at 0-5° C to form compound ‘C’. On treating C with \[\ce{H3PO2}\], it gets converted to D with formula \[\ce{C7H8}\], which on further reaction with \[\ce{CrO2Cl2}\] followed by hydrolysis forms ‘E’ \[\ce{C7H6O}\]. Write the structure of compounds A to E. Write the chemical equations involved.
