Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2023-2024
Date: March 2024
Advertisements
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Question paper is divided into FIVE sections - Section A, B, C, D and E.
- Section A: Question number 1 to 12 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) type questions and 13 to 16 are Assertion Reasoning based carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B: Question number 17 to 21 are Very Short Answer (VSA) type questions carrying 2 marks each.
- Section C: Question number 22 to 28 are Short Answer (SA) type questions carrying 3 marks each
- Section D: Question number 29 to 30 are Case-Based questions carrying 4 marks each.
- Section E: Question number 31 and 33 are Long Answer (LA) type questions carrying 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question in Section B, one question in Section C, one question in Section D and all three questions in Section E. You have to attempt only one of the choices in such questions.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed.
Which of the following solutions will have the highest conductivity at 298 K?
0.01 M HCl solution
0.1 M HCl solution
0.01 M CH3COOH solution
0.1 M CH3COOH solution
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry

Identify A and B:
A = 1-phenylethanal , B = acetophenone
A = Benzophenone B = formaldehyde
A = Benzaldehyde , B = Acetophenone
A = Benzophenone, B = Acetophenone
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
The vitamins which can be stored in our body are ______.
Vitamin A, B, D and E
Vitamin A, C, D and K
Vitamin A, B, C and D
Vitamin A, D, E and K
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
What is IUPAC name of the ketone A, which undergoes iodo form reaction to give \[\ce{CH3CH = C(CH3)COONa}\] and yellow precipitate of \[\ce{CH3}\]?
3-Methylpent-3-en-2one
3-Methylbut-2-en- one
2, 3-Dimethylethanone
3-Methylpent-4-one
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Which of the following is not correct?
In haloarenes, the electron pairs on halogen atom are in conjugation with π-electrons of the ring.
The carbon-magnesium bond is covalent and non-polar in nature.
During `"S"_("N"^1)` reaction, the carbocation formed in the slow step being sp2 hybridised is planar.
Out of \[\ce{CH2= CH-Cl and C6H5CH2Cl, C6H5CH2Cl}\] is more reactive towards `"S"_("N"^1)` reaction.
Chapter: [0.01] Solid State
Match the properties with the elements of 3d series:
| (i) | lowest enthalpy of atomisation | (p) | Sc |
| (ii) | shows maximum number of oxidation states | (q) | Mn |
| (iii) | transition metal that does not form coloured compounds |
(r) | Zn |
| (s) | Ti |
(i) (r), (ii) (q), (iii) (p)
(i) (r), (ii) (s), (iii) (p)
(i) (p), (ii) (q), (iii) (r)
(i) (s), (ii) (r), (iii) (p)
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Which of the following statement is true?
Molecularity of reaction can be zero or a fraction.
Molecularity has no meaning for complex reactions.
Molecularity of a reaction is an experimental quantity.
Reactions with the molecularity three are very rare but are fast.
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
In which of the following solvents, the \[\ce{C4H8NH3+X–}\] is soluble?
ether
acetone
water
bromine water
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Which of the following observation is shown by 2-phenyl ethanol with Lucas Reagent?
Turbidity will be observed within five minutes.
No turbidity will be observed.
Turbidity will be observed immediately.
Turbidity will be observed at room temperature but will disappear after five minutes.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
If the initial concentration of substance A is 1.5 M and after 120 seconds the concentration of substance A is 0.75 M, the rate constant for the reaction if it follows zero-order kinetics is ______.
0.00625 molL-1s-1
0.00625 s-1
0.00578 molL-1s-1
0.00578 s-1
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Anisole undergoes bromination with bromine in ethanoic acid even in the absence of iron (III) bromide catalyst.
Due to the activation of benzene ring by the methoxy group.
Due to the de-activation of benzene ring by the methoxy group.
Due to the increase in electron density at ortho and para positions.
Due to the formation of stable carbocation.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
The trend of which property is represented by the following graph?
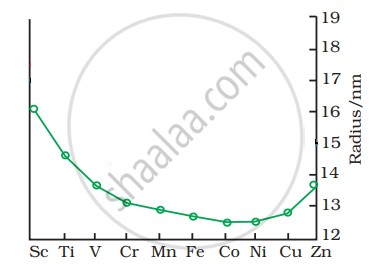
ionization enthalpy
atomic radii
enthalpy of atomization
melting point
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Assertion (A): Alcohols react both as nucleophiles and electrophiles.
Reason (R): The bond between C–O is broken when alcohols react as nucleophiles.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Assertion (A): Strong oxidising agents oxidise toluene and its derivatives to benzoic acids.
Reason (R): It is possible to stop the oxidation of toluene at the aldehyde stage with suitable reagents.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Assertion: Enzymes are very specific for a particular reaction and for a particular substrate.
Reason: Enzymes are biocatalysts.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Assertion (A): During electrolysis of aqueous copper sulphate solution using copper electrodes hydrogen gas is released at the cathode.
Reason (R): The electrode potential of Cu2+/Cu is greater than that of H+/H2.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
A is true but R is false.
A is false but R is true.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Radioactive decay follows first-order kinetics. The initial amount of two radioactive elements X and Y is 1 gm each. What will be the ratio of X and Y after two days if their half-lives are 12 hours and 16 hours respectively?
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
The hypothetical reaction \[\ce{P + Q -> R}\] is half order w.r.t ‘P’ and zero order w.r.t ‘Q’. What is the unit of rate constant for this reaction?
Chapter:
A 5% solution of \[\ce{Na2SO4.10H2O}\] (MW = 3 22) is isotonic with 2% solution of non- electrolytic, non volatile substance X. Find out the molecular weight of X.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Arrange the isomeric dichlorobenzene in the increasing order of their boiling point and melting points.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Explain why the electrophilic substitution reactions in haloarenes occur slowly and require more drastic conditions as compared to those in benzene.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Advertisements
Out of p-tolualdehyde and p-nitrobenzaldehyde, which one is more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions, why?
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Write the structure of the product formed when acetone reacts with 2, 4 DNP reagent.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Convert the following:
Benzene to m-nitrobenzaldehyde
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Convert the following:
Bromobenzene to benzoic acid
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
DNA fingerprinting is used to determine paternity of an individual. Which property of DNA helps in the procedure?
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
What structural change will occur when a native protein is subjected to change in pH?
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Write the formula for the following coordination compound.
Bis (ethane-1,2-diamine) dihydroxidochromium (III) chloride
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Does ionization isomer for the following compound exist? Justify your answer.
\[\ce{Hg[Co(SCN)4]}\]
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Is the central metal atom in coordination complexes a Lewis acid or a Lewis base? Explain.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Can we construct an electrochemical cell with two half-cells composed of ZnSO4 solution and zinc electrodes? Explain your answer.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Calculate the λ0m for Cl- ion from the data given below:
∧0m MgCl2 = 258.6 Scm2 mol-1 and λ0m Mg2+ = 106 Scm2 mol-1
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
The cell constant of a conductivity cell is 0.146 cm-1. What is the conductivity of 0.01 M solution of an electrolyte at 298 K, if the resistance of the cell is 1000 ohm?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Write the name of the reaction, structure and IUPAC name of the product formed when:
Phenol reacts with CHCl3 in the presence of NaOH followed by hydrolysis.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the name of the reaction, structure and IUPAC name of the product formed when:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH(CH3) ONa}\] reacts with \[\ce{C2H5Br}\]
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the name of the reaction, structure and IUPAC name of the product formed when:
CH3CH2CN reacts with stannous chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid, followed by hydrolysis.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
You are given four organic compounds “A”, “B” , “C” and “D”. The compounds “A”, “B” and “C” form an orange-red precipitate with 2, 4 DNP reagent. Compounds “A” and “B” reduce Tollen’s reagent while compounds “C” and “D” do not. Both “B” and “C” give a yellow precipitate when heated with iodine in the presence of NaOH. Compound “D” gives brisk effervescence with sodium bicarbonate solution. Identify “A”, “B”, “C” and “D” given the number of carbon atoms in three of these carbon compounds is three while one has two carbon atoms. Give an explanation for our answer.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
When sucrose is hydrolysed the optical rotation values are measured using a polarimeter and are given in the following table:
| S. No. | Time (hours) | Specific Rotation |
| 1 | 0 | + 66.5° |
| 2 | ∞ | - 39.9° |
- Account for the two specific rotation values.
- What is the specific name given to sucrose based on the above observation?
- One of the products formed during the hydrolysis of sucrose is a glucose, that reacts with hydroxylamine to give compound A. Identify compound A.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
An organic compound A with the molecular formula (+) C4H9Br undergoes hydrolysis to form (+) C4H9OH. Give the structure of A and write the mechanism of the reaction.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
The rate constants of a reaction at 200 K and 500 K are 0.02 s–1 and 0.20 s–1 respectively. Calculate the value of Ea (Given 2.303 R = 19.15 JK-1 mol-1).
Chapter:
Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
|
Crystal field splitting by various ligands Metal complexes show different colours due to d-d transitions. The complex absorbs light of specific wavelength to promote the electron from t2g to eg level. The colour of the complex is due to the transmitted light, which is complementary of the colour absorbed. The wave number of light absorbed by different complexes of Cr ion are given below:
|
Answer the following questions:
(a) Out of ligands "A", "B", "C" and "D", which ligand causes maximum crystal field splitting? Why?
OR
Which of the two, “A” or “D” will be a weak field ligand? Why?
(b) Which of the complexes will be violet in colour? [CrA6]3- or [CrB6]3+ and why?
(Given: If 560 - 570 nm of light is absorbed, the colour of the complex observed is violet.)
(c) If the ligands attached to Cr3+ ion in the complexes given in the table above are water, cyanide ion, chloride ion, and ammonia (not in this order).
Identify the ligand, write the formula and IUPAC name of the following:
- [CrA6]3-
- [CrC6]3+
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Advertisements
Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
|
The lead-acid battery represents the oldest rechargeable battery technology. Lead acid batteries can be found in a wide variety of applications including small-scale power storage such as UPS systems, ignition power sources for automobiles, along with large, grid-scale power systems. The spongy lead act as the anode and lead dioxide as the cathode. Aqueous sulphuric acid is used as an electrolyte. The half-reactions during discharging of lead storage cells are: Anode: \[\ce{Pb(s) + SO^{2-}_4 (aq) -> PbSO4 (s) + 2e-}\] Cathode: \[\ce{PbO (s) + 4H+ (aq) + SO^{2-}_4 (aq) + 2e- -> PbSO(s) + 2 H2O}\] There is no safe way of disposal and these batteries end - up in landfills. Lead and sulphuric acid are extremely hazardous and pollute soil, water as well as air. Irrespective of the environmental challenges it poses, lead-acid batteries have remained an important source of energy. Designing green and sustainable battery systems as alternatives to conventional means remains relevant. Fuel cells are seen as the future source of energy. Hydrogen is considered a green fuel. Problem with fuel cells at present is the storage of hydrogen. Currently, ammonia and methanol are being used as a source of hydrogen for fuel cell. These are obtained industrially, so add to the environmental issues. If the problem of storage of hydrogen is overcome, is it still a “green fuel?” Despite being the most abundant element in the Universe, hydrogen does not exist on its own so needs to be extracted from the water using electrolysis or separated from carbon fossil fuels. Both of these processes require a significant amount of energy which is currently more than that gained from the hydrogen itself. In addition, this extraction typically requires the use of fossil fuels. More research is being conducted in this field to solve these problems. Despite the problem of no good means to extract Hydrogen, it is a uniquely abundant and renewable source of energy, perfect for our future zero-carbon needs. |
Answer the following questions:
- How many coulombs have been transferred from anode to cathode in order to consume one mole of sulphuric acid during the discharging of lead storage cell?
- How much work can be extracted by using lead storage cell if each cell delivers about 2.0 V of voltage? (1 F = 96500 C)
- Do you agree with the statement – “Hydrogen is a green fuel.” Give your comments for and against this statement and justify your views.
OR
Imagine you are a member of an agency funding scientific research. Which of the following projects will you fund and why?
- safe recycling of lead batteries
- extraction of hydrogen
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Which of the following ions will have a magnetic moment value of 1.73 BM.
\[\ce{Sc^3+, Ti^3+, Ti^2+, Cu^2+, Zn^2+}\]
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
In order to protect iron from corrosion, which one will you prefer as a sacrificial electrode, Ni or Zn? Why? (Given standard electrode potentials of Ni, Fe and Zn are -0.25 V, -0.44 V and -0.76 V respectively.)
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
The second ionization enthalpies of chromium and manganese are 1592 and 1509 kJ/mol respectively. Explain the lower value of Mn.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Give two similarities in the properties of Sc and Zn.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
What is actinoid contraction?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
What causes actinoid contraction?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
What is the oxidation state of chromium in chromate ion and dichromate ion?
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Write the ionic equation for reaction of KI with acidified KMnO4.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
What is the effect of temperature on the solubility of glucose in water?
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Ibrahim collected 10 mL each of fresh water and ocean water. He observed that one sample labeled “P” froze at 0° C while the other “Q” at -1.3° C. Ibrahim forgot which of the two, “P” or “Q” was ocean water. Help him identify which container contains ocean water, giving rationalization for your answer.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Calculate Van't Hoff factor for an aqueous solution of K3 [Fe(CN)6] if the degree of dissociation (α) is 0.852. What will be boiling point of this solution if its concentration is 1 molal? (Kb = 0.52 K kg/mol)
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
What type of deviation from Roult’s Law is expected when phenol and aniline are mixed with each other? What change in the net volume of the mixture is expected? Graphically represent the deviation.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
The vapour pressure of pure water at a certain temperature is 23.80 mm Hg. If 1 mole of a non-volatile non-electrolytic solute is dissolved in 100g water, Calculate the resultant vapour pressure of the solution.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
An organic compound with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H7NO2}\] exists in three isomeric forms, the isomer ‘A’ has the highest melting point of the three. ‘A’ on reduction gives compound ‘B’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C7H9N}\]. ‘B’ on treatment with \[\ce{NaNO2/HCl}\] at 0-5° C to form compound ‘C’. On treating C with \[\ce{H3PO2}\], it gets converted to D with formula \[\ce{C7H8}\], which on further reaction with \[\ce{CrO2Cl2}\] followed by hydrolysis forms ‘E’ \[\ce{C7H6O}\]. Write the structure of compounds A to E. Write the chemical equations involved.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Account for the following:
N-ethylbenzene sulphonyl amide is soluble in alkali.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Account for the following:
Reduction of nitrobenzene using Fe and HCl is preferred over Sn and HCl.
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Arrange the decreasing order of pKb values.
\[\ce{C6H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, C6H5CH2NH2, CH3NH2, NH3}\]
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Arrange the increasing order of solubility in water.
\[\ce{C2H5Cl, C2H5NH2, C2H5OH}\]
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Arrange the decreasing boiling point.
\[\ce{CH3COOH, C2H5OH, CH3NH2, CH3OCH3}\]
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2023 - 2024
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2024 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
