Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How will you distinguish 1° and 2° hydroxyl groups present in glucose? Explain with reactions.
Solution
On oxidation with nitric acid, glucose as well as gluconic acid both yield a dicarboxylic acid, saccharic acid. This indicates the presence of a primary alcoholic (–OH) group in glucose.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.......}\ce{CHO}\phantom{..............}\ce{COOH}\phantom{............}\ce{COOH}\phantom{....}\\
\phantom{......}|\phantom{...................}|\phantom{..................}|\phantom{........}\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{(CHOH)4 ->[Oxidation] (CHOH)4 <-[Oxidation] (CHOH)4}\\
\phantom{......}|\phantom{...................}|\phantom{..................}|\phantom{........}\\
\phantom{......}\ce{CH2OH}\phantom{............}\ce{\underset{acid}{\underset{Saccharic}{COOH}}\phantom{............}\ce{\underset{acid}{\underset{Gluconic}{CH2OH}}}\phantom{..}}\\
\end{array}\]
Acetylation of glucose with acetic anhydride gives glucose pentaacetate which confirms the presence of five –OH groups. Since it exists as a stable compound, five –OH groups should be attached to different carbon atoms.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{...}\ce{CHO}\phantom{..................}\ce{CHO}\phantom{......}\ce{O}\phantom{..........}\\
\phantom{........}|\phantom{.......................}|\phantom{..........}||\phantom{...............}\\
\phantom{}\ce{(CHOH)4 ->[Acetic anhydride] (CH - O - C - CH3)4}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{.......................}|\phantom{...................}\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{CH2OH}\phantom{................}\ce{CH2 - O - C - CH3}
\phantom{.....}\\
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What happens when glucose is treated with hydroxylamine?
Maltose is a
(a) Polysaccharide
(b) Disaccharide
(c) Trisaccharide
(d) Monosaccharide
Glucose on reaction with HI gives n-hexane. What does it suggest about the structure of glucose?
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
(iodoform, acetaldehyde, positive, greater, acidic, acetone, disaccharide, negative, increases, glucose, decreases, chloroform, polysaccharide, lactose, lesser, basic, cationic hydrolysis, anionic hydrolysis)
Sucrose is a _________ and yields upon hydrolysis, a mixture of ________ and fructose.
The following compound can be called as:
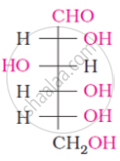
The spatial arrangement of the given molecule is denoted by:

What is the most abundant organic compound on earth?
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding glucose?
The number of chiral carbons in ß-D(+) glucose is ____________.
In the following reaction, identify A and B:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C6H12O6 ->[Acetic anhydride] A}\\
\downarrow \text{Conc. nitric acid}\phantom{...}\\
\ce{B}\phantom{.................}\end{array}\]
