Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Alcohols react with active metals e.g. Na, K etc. to give corresponding alkoxides. Write down the decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal towards primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Solution
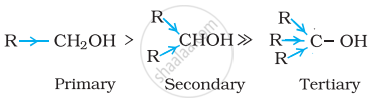
Decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal is:
1° > 2° > 3°
Alcohols react with sodium metal to form alkoxides and hydrogen is liberated:
\[\ce{R - O - H + Na -> RO - Na+ {+} 1/2 H2}\]
The order of reactivity of alcohols is primary > secondary > tertiary. This can be explained on the basis of cleavage of O – H bond. The alkyl groups are electron releasing groups (+I effect) and they increase the electron density around the oxygen. As a result, the electrons of O – H bond cannot be withdrawn strongly towards oxygen and O – H remains strong. Therefore, greater is the number, of alkyl groups present, smaller will be reactivity of alcohol.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give reasons for the following:
o-nitrophenol is more acidic than o-methoxyphenol.
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Lucas test is used for the detection of _____________.
Which of the following is not true in case of reaction with heated copper at 300°C?
Lucas test is done to differentiate between ____________.
The compound which gives the most stable carbonium ion on dehydration is:
During dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with cone. H2SO4 the initial step is ____________.
Assertion: Bond angle in ethers is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle.
Reason: There is a repulsion between the two bulky (–R) groups.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene
