Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Alcohols react with active metals e.g. Na, K etc. to give corresponding alkoxides. Write down the decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal towards primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
उत्तर
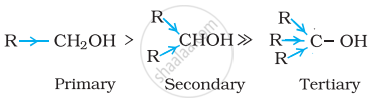
Decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal is:
1° > 2° > 3°
Alcohols react with sodium metal to form alkoxides and hydrogen is liberated:
\[\ce{R - O - H + Na -> RO - Na+ {+} 1/2 H2}\]
The order of reactivity of alcohols is primary > secondary > tertiary. This can be explained on the basis of cleavage of O – H bond. The alkyl groups are electron releasing groups (+I effect) and they increase the electron density around the oxygen. As a result, the electrons of O – H bond cannot be withdrawn strongly towards oxygen and O – H remains strong. Therefore, greater is the number, of alkyl groups present, smaller will be reactivity of alcohol.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following are used to convert RCHO into RCH2OH?
(i) H2/Pd
(ii) LiAlH4
(iii) NaBH4
(iv) Reaction with RMgX followed by hydrolysis
Lucas test is done to differentiate between ____________.
During dehydration of alcohols to alkenes by heating with cone. H2SO4 the initial step is ____________.
Identify the secondary alcohols from the following set:
- \[\ce{CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3}\]
- \[\ce{(C2H5)3COH}\]
What happens when (CH3)3 C – OH is heated with Cu/573 K?
Write the chemical equation in support of your answer.
Which of the following observation is shown by 2-phenyl ethanol with Lucas Reagent?
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
