Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Alcohols react with active metals e.g. Na, K etc. to give corresponding alkoxides. Write down the decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal towards primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
उत्तर
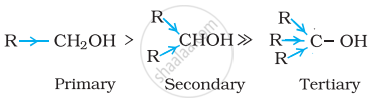
Decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal is:
1° > 2° > 3°
Alcohols react with sodium metal to form alkoxides and hydrogen is liberated:
\[\ce{R - O - H + Na -> RO - Na+ {+} 1/2 H2}\]
The order of reactivity of alcohols is primary > secondary > tertiary. This can be explained on the basis of cleavage of O – H bond. The alkyl groups are electron releasing groups (+I effect) and they increase the electron density around the oxygen. As a result, the electrons of O – H bond cannot be withdrawn strongly towards oxygen and O – H remains strong. Therefore, greater is the number, of alkyl groups present, smaller will be reactivity of alcohol.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
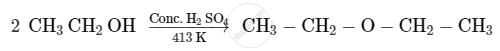
Give the equation of the following reaction:
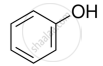
Treating phenol with chloroform in the presence of aqueous NaOH.
In the reduction \[\ce{R - CHO + H2 -> RCH2OH}\] the catalyst used is:
Which of the following is not true in case of reaction with heated copper at 300°C?
The compound which gives the most stable carbonium ion on dehydration is:
Cyclohexene is best prepared from cyclohexanol by which of the following:
Identify the secondary alcohols from the following set:
- \[\ce{CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3}\]
- \[\ce{(C2H5)3COH}\]
Ethers can be prepared by Williamson synthesis in which an alkyl halide is reacted with sodium alkoxide. Di-tert-butyl ether can’t be prepared by this method. Explain.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
