Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Solution
The mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene involves the following three steps:
Step 1: Protonation of ethanol to form ethyl oxonium ion:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{.........................}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{..........................}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{..}\\
\ce{H - C - C - \overset{\bullet\bullet}{\underset{\bullet\bullet}{O}} - H + H^+ ⇌[Fast] H - C - C - \underset{\bullet\bullet\phantom{...}}{O^+} - H}\\
\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{..........................}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{..........}\\
\ce{\underset{Ethanol}{H\phantom{...}H}}\phantom{.....................}\ce{\underset{(Ethyl oxonium ion)}{\underset{Protonated alcohol}{H\phantom{...}H}}}\phantom{..}
\end{array}\]
Step 2: Formation of carbocation (rate determining step): It is the slowest step and hence the rate-determining step of the reaction.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...............}\ce{H}\phantom{....}\ce{H}\phantom{....}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{................}|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{H - C - C - \underset{\bullet\bullet\phantom{...}}{O^+} - H <=>[Slow] H - C - C^+ + H2O}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{.....................}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{....................}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{....}
\end{array}\]
Step 3: Elimination of a proton to form ethene:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{....}\ce{H}\phantom{........}\ce{H}\phantom{.}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{......}\backslash\phantom{......}/\\
\ce{H - C - C^+ <=> C = C + H^+}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{......}/\phantom{......}\backslash\\
\phantom{..}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{....}\ce{\underset{Ethene}{H\phantom{........}H}}\phantom{.}
\end{array}\]
The acid consumed in step 1 is released in Step 3. After the formation of ethene, it is removed to shift the equilibrium in a forward direction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the final product(s) in each of the following reactions:
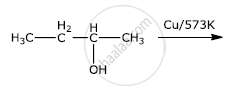
Show how will you synthesize pentan-1-ol using a suitable alkyl halide.
Give the equation of the following reaction:
Dilute HNO3 with phenol.
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Oxidation of a primary alcohol to carboxylic acid.
Lucas reagent is ____________.
Dehydration of 2-butanol yields:
Lucas test is done to differentiate between ____________.
Which one of the following on oxidation gives a ketone?
Primary and secondary alcohols on the action of reduced copper give:
The compound which gives the most stable carbonium ion on dehydration is:
Cyclohexene is best prepared from cyclohexanol by which of the following:
The process of converting alkyl halides into alcohols involves ______.
Name the factors responsible for the solubility of alcohols in water.
The correct geometry around oxygen in CH3OCH3 is
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
