Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Solutions
3: Electrochemistry
4: Chemical Kinetics
5: Surface Chemistry
6: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
7: The p-block Elements
8: The d-block and f-block Elements
9: Coordinate Compounds
10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
▶ 11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
13: Amines
14: Biomolecules
15: Polymers
16: Chemistry in Everyday Life
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 11 of CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC NCERT for Chemistry [English] Class 12.
NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Intext Questions [Pages 317 - 343]
Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2OH}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}
\end{array}\]
Primary alcohol
Secondary alcohol
Tertiary alcohol
Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol:
H2C = CH – CH2OH
Primary alcohol
Secondary alcohol
Tertiary alcohol
Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol:
CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – OH
Primary alcohol
Secondary alcohol
Tertiary alcohol
Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol:
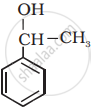
Primary alcohol
Secondary alcohol
Tertiary alcohol
Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol:
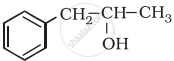
Primary alcohol
Secondary alcohol
Tertiary alcohol
Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol:
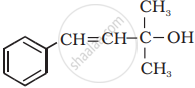
Primary alcohol
Secondary alcohol
Tertiary alcohol
Identify allylic alcohols in the following examples.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2OH}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}
\end{array}\]H2C = CH – CH2OH
CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – OH

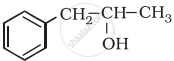
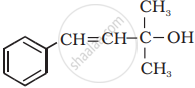
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{............}\ce{CH2OH}\\
\phantom{......}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH - CH - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{......}|\phantom{............}|\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{........}\ce{CH2Cl}\phantom{......}\ce{CH3}\phantom{}
\end{array}\]
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{........................}\ce{CH2OH}\\
\phantom{..................}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH2 - CH - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{.............}|\phantom{........}\\
\phantom{..}\ce{CH3}\phantom{..........}\ce{OH}\phantom{........}
\end{array}\]
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system.
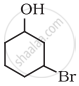
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H2C = CH - CH - CH2 - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{..........}\\
\ce{OH}\phantom{........}
\end{array}\]
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - C = C - CH2OH}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\ce{Br}\phantom{...}
\end{array}\]
Show how is the following alcohol prepared by the reaction of a suitable Grignard reagent on methanal?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH2OH}\\
|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{...}
\end{array}\]
Show how is the following alcohol prepared by the reaction of a suitable Grignard reagent on methanal?
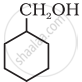
\[\ce{CH3 - CH = CH2 ->[H2O/H^+]}\]
Write the structure of the product of the following reaction:
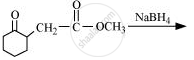
Write the structure of the product of the following reaction:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH - CHO ->[NaBH4]}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.}
\end{array}\]
Give the structure of the product you would expect when the following alcohol reacts with HCl–ZnCl2.
Butan-1-ol
Give the structure of the product you would expect when the following alcohol reacts with HCl–ZnCl2.
2-Methylbutan-2-ol
Predict the major product of acid catalysed dehydration of 1-methylcyclohexanol.
Predict the major product of acid catalysed dehydration of butan-1-ol.
Ortho and para nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol. Draw the resonance structures of the corresponding phenoxide ions.
Write the equation involved in the following reaction:
Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Write the equation involved in the following reaction:
Kolbe’s reaction
Write the reactions of Williamson synthesis of 2-ethoxy-3-methylpentane starting from ethanol and 3-methylpentan-2-ol.
Which of the following is an appropriate set of reactants for the preparation of 1-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene and why?
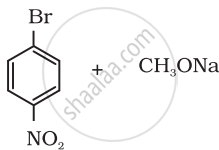 |
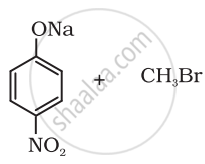 |
| (i) | (ii) |
Predict the product of the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - O - CH3 + HBr ->}\]
Predict the product of the following reaction:
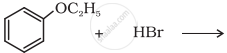
Predict the product of the following reaction:
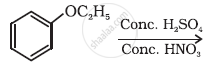
Predict the product of the following reaction:
\[\ce{(CH3)3C - OC2H5 ->[HI]}\]
NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Exercises [Pages 344 - 346]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{................}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{.............}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - C - CH3}\\
|\phantom{......}|\phantom{......}|\\
\phantom{...}\ce{CH3\phantom{.}}\phantom{..}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H3C - CH - CH2 - CH - CH - CH2 - CH3}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{.............}|\phantom{......}|\phantom{.........}\\
\phantom{}\ce{OH}\phantom{..........}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{C2H5}\phantom{......}
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - CH3}\\
|\phantom{......}|\phantom{..}\\
\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{OH}\phantom{}
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{HO - CH2 - CH - CH2 - OH}\\
|\phantom{..}\\
\ce{OH}
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
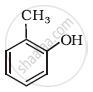
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
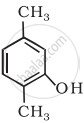
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
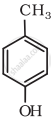
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
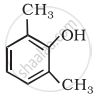
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - O - CH2 - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{..........}|\\
\phantom{............}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
C6H5 – O – C2H5
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
C6H5 – O – C7H15(n−)
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH2 - O - CH - CH2 - CH3}\\
\phantom{...}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
Write the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is as follows:
2-Methylbutan-2-ol
Write structures of the compounds whose IUPAC names are as follows:
3-Chloromethylpentan-1-ol.
Write the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is as follows:
1-Phenylpropan-2-ol
Write the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is as follows:
3, 5-Dimethylhexane−1, 3, 5-triol
Write the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is as follows:
2, 3-Diethylphenol
Write the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is as follows:
1-Ethoxypropane
Write the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is as follows:
2-Ethoxy-3-methylpentane
Write the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is as follows:
Cyclohexylmethanol
Write the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is as follows:
3-Cyclohexylpentan-3-ol
Write the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is as follows:
Cyclopent-3-en-1-ol
- Draw the structures of all isomeric alcohols of molecular formula C5H12O and give their IUPAC names.
- Classify the isomers of alcohols in the above question as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Explain why propanol has higher boiling point than that of the hydrocarbon, butane?
Alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses. Explain this fact.
What is meant by hydroboration-oxidation reaction? Illustrate it with an example.
Give the structures and IUPAC names of monohydric phenols of molecular formula C7H8O.
While separating a mixture of ortho and para nitrophenols by steam distillation, name the isomer which will be steam volatile. Give reason.
Give the equations of reactions for the preparation of phenol from cumene.
Write chemical reaction for the preparation of phenol from chlorobenzene.
Write the mechanism of hydration of ethene to yield ethanol.
You are given benzene, conc. H2SO4 and NaOH. Write the equations for the preparation of phenol using these reagents.
Show how will you synthesize 1-phenylethanol from a suitable alkene.
Show how will you synthesize cyclohexylmethanol using an alkyl halide by an SN2 reaction.
Show how will you synthesize pentan-1-ol using a suitable alkyl halide.
Give two reactions that show the acidic nature of phenol.
Compare acidity of phenol with that of ethanol.
Give reasons for the following:
o-nitrophenol is more acidic than o-methoxyphenol.
Explain how does the −OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring activate it towards electrophilic substitution?
Give the equation of the following reaction:
Oxidation of propan-1-ol with alkaline KMnO4 solution.
Give the equation of the following reaction:
Bromine in CS2 with phenol.
Give the equation of the following reaction:
Dilute HNO3 with phenol.
Give the equation of the following reaction:
Treating phenol with chloroform in the presence of aqueous NaOH.
Explain the following with an example.
Kolbe’s reaction.
Write the equation involved in the following reaction:
Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Explain the following with an example.
Williamson ether synthesis
Explain the following with an example.
Unsymmetrical ether
Write the mechanism of acid-catalysed dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
How is the following conversion carried out?
\[\ce{Propene -> Propan-2-ol}\]
How is the following conversion carried out?
\[\ce{Benzyl chloride -> Benzyl alcohol}\]
How is the following conversion carried out?
\[\ce{Ethyl magnesium chloride -> Propan-1-ol}\]
How is the following conversion carried out?
\[\ce{Methyl magnesium bromide → 2-Methylpropan-2-ol}\]
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Oxidation of a primary alcohol to carboxylic acid.
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Oxidation of a primary alcohol to aldehyde.
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Bromination of phenol to 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol.
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid.
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Dehydration of propan-2-ol to propene.
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Butan-2-one to butan-2-ol.
Give reason for the higher boiling point of ethanol in comparison to methoxymethane.
Give IUPAC name of the following ether:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C2H5OCH2 - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\phantom{.......}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
Give IUPAC name of the following ether:
CH3OCH2CH2Cl
Give IUPAC name of the following ether:
O2N – C6H4 – OCH3(p)
Write the name of the reagent and equation for the preparation of the following ethers by Williamson’s synthesis:
1-Methoxyethane
Give IUPAC name of the following ether:
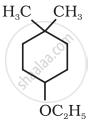
Give IUPAC name of the following ether:
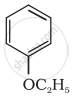
Write the name of the reagent and the equation for the preparation of the following ether by Williamson’s synthesis:
1-Propoxypropane
Write the name of the reagent and the equation for the preparation of the following ether by Williamson’s synthesis:
Ethoxybenzene
Write the name of the reagent and the equation for the preparation of the following ether by Williamson’s synthesis:
2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane
Illustrate with examples the limitations of Williamson synthesis for the preparation of certain types of ethers.
How is 1-propoxypropane synthesised from propan-1-ol? Write mechanism of this reaction.
Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohols is not a suitable method. Give reason.
Write the equation of the reaction of hydrogen iodide with 1-propoxypropane.
Write the equation of the reaction of hydrogen iodide with methoxybenzene.
Write the equation of the reaction of hydrogen iodide with benzyl ethyl ether.
Explain the fact that in aryl alkyl ethers
- the alkoxy group activates the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution and
- it directs the incoming substituents to ortho and para positions in the benzene ring.
Write the mechanism of the reaction of HI with methoxymethane.
Write the equation of the following reaction:
Friedel-Crafts reaction - alkylation of anisole
Write the equation of the following reaction:
Nitration of anisole.
Write the equation of the following reaction:
Bromination of anisole in an ethanoic acid medium.
Write the equation of the following reaction:
Friedel-Craft’s acetylation of anisole.
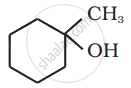
Show how you would synthesise the following alcohol from an appropriate alkene?
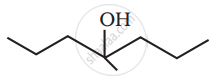
Show how you would synthesise the following alcohol from an appropriate alkene?
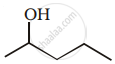
Show how you would synthesise the following alcohol from an appropriate alkene?
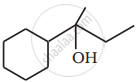
When 3-methylbutan-2-ol is treated with HBr, the following reaction takes place:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.......................}\ce{Br}\\
\phantom{......................}|\\
\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - CH3 ->[HBr] CH3 - C - CH2 - CH3}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{......}|\phantom{......................}|\phantom{........}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\phantom{...}\ce{OH}\phantom{...................}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.....}
\end{array}\]
Give a mechanism for this reaction.
(Hint: The secondary carbocation formed in step II rearranges to a more
stable tertiary carbocation by a hydride ion shift from 3rd carbon atom.)
Solutions for 11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC 11 (Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers are Classification of Alcohols and Phenols, Nomenclature, Physical and Chemical Properties of Alcohols and Phenols, Preparation of Commercially Important Alcohols, Classification of Ethers, Structures of Functional Groups of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers, Methods of Preparation of Alcohols, Methods of Preparation of Phenols, Reactions Involving Cleavage of O-H Bond, Reactions Involving Cleavage of Carbon–Oxygen (C–O) Bond in Alcohols, Chemical Properties of Phenol, Preparation of Ethers, Physical Properties of Ethers, Chemical Reaction of Ethers - Cleavege of C-O Bonds, Chemical Reaction of Ethers - Electrophilic Substitution, Classification of Alcohols and Phenols, Nomenclature, Physical and Chemical Properties of Alcohols and Phenols, Preparation of Commercially Important Alcohols, Classification of Ethers, Structures of Functional Groups of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers, Methods of Preparation of Alcohols, Methods of Preparation of Phenols, Reactions Involving Cleavage of O-H Bond, Reactions Involving Cleavage of Carbon–Oxygen (C–O) Bond in Alcohols, Chemical Properties of Phenol, Preparation of Ethers, Physical Properties of Ethers, Chemical Reaction of Ethers - Cleavege of C-O Bonds, Chemical Reaction of Ethers - Electrophilic Substitution.
Using NCERT Chemistry [English] Class 12 solutions Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Chemistry [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 11, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Chemistry [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
![NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - Shaalaa.com](/images/9788174506481-chemistry-english-class-12_6:a55896f658974483bc7dc0613af00ce2.jpg)
