Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Solutions
3: Electrochemistry
4: Chemical Kinetics
5: Surface Chemistry
6: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
7: The p-block Elements
8: The d-block and f-block Elements
9: Coordinate Compounds
10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
▶ 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
13: Amines
14: Biomolecules
15: Polymers
16: Chemistry in Everyday Life
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 12 of CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC NCERT for Chemistry [English] Class 12.
NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Intext Questions [Pages 353 - 376]
Write the structure of the following compound:
α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
Write the structure of the following compound:
3-Hydroxybutanal
Write the structure of the following compound:
2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
Write the structure of the following compound:
4-Oxopentanal
Write the structure of the following compound:
Di-sec-butyl ketone
Write the structure of the following compound:
4-Fluoroacetophenone
Write the structure of the product of the following reaction:
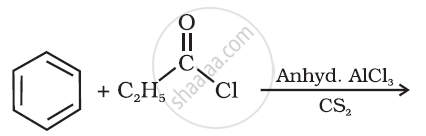
Write the structure of the product of the following reaction:
\[\ce{(C6H5CH2)2 Cd + 2 CH3COCl ->}\]
Write the structure of the product of the following reaction:
\[\ce{H3C - C ≡ C - H ->[Hg^{2+}, H2SO4]}\]
Write the structure of the product of the following reaction:
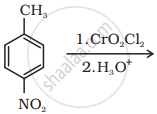
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.
CH3CHO, CH3CH2OH, CH3OCH3, CH3CH2CH3
Arrange the following compound in increasing order of its reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions.
Ethanal, Propanal, Propanone, Butanone.
Hint: Consider steric effect and electronic effect.
Arrange the following compound in increasing order of its reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions.
Benzaldehyde, p-Tolualdehyde, p-Nitrobenzaldehyde, Acetophenone.
Hint: Consider steric effect and electronic effect.
Predict the product of the following reaction:
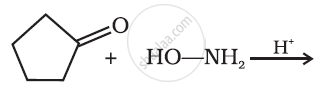
Predict the product of the following reaction:
Predict the product of the following reaction:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..............}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{..............}||\\
\ce{R - CH = CH - CHO + NH2 - C - NH - NH2 ->[H+]}\end{array}\]
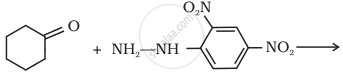
Predict the product of the following reaction:
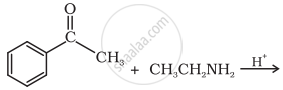
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
PhCH2CH2COOH
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
(CH3)2C=CHCOOH
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
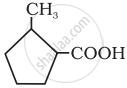
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
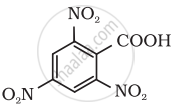
Show how the following compound can be converted to benzoic acid.
Ethylbenzene
Show how the following compound can be converted to benzoic acid.
Acetophenone
Show how the following compound can be converted to benzoic acid.
Bromobenzene
Show how the following compound can be converted to benzoic acid.
Phenylethene (Styrene)
CH3CO2H or CH2FCO2H
Which acid of the pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
Which acid of the pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
Which acid of the pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
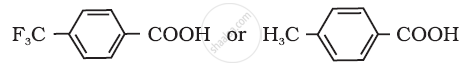
NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Exercises [Pages 377 - 379]
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Cyanohydrin
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Acetal
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Semicarbazone
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Aldol
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Hemiacetal
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Oxime
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Ketal
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Imine
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
2, 4-DNP-derivative
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction in the following case.
Schiff’s base
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2CHO
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
CH3CH2COCH(C2H5)CH2CH2Cl
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
CH3CH=CHCHO
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
CH3COCH2COCH3
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
CH3CH(CH3)CH2C(CH3)2COCH3
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
OHCC6H4CHO-p
Draw the structure of the following compound.
3-Methylbutanal
Draw the structure of the following compound.
p-Nitropropiophenone
Write the structure of p-methylbenzaldehyde.
Draw the structure of the following compound.
4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
Write the structure of 4-chloropentan-2-one.
Draw the structure of the following compound.
3-Bromo-4-phenylpentanoic acid
Draw the structure of the following compound.
p, p’-Dihydroxybenzophenone
Draw the structure of the following compound.
Hex-2-en-4-ynoic acid
Write the IUPAC name of the following ketone or aldehyde. Wherever possible, give also the common name.
CH3CO(CH2)4CH3
Write the IUPAC name of the following ketone or aldehyde. Wherever possible, give also the common name.
CH3CH2CHBrCH2CH(CH3)CHO
Write the IUPAC name of the following ketone or aldehyde. Wherever possible, give also the common name.
CH3(CH2)5CHO
Write the IUPAC name of the following ketone or aldehyde. Wherever possible, give also the common name.
Ph-CH=CH-CHO
Write the IUPAC name of the following ketone or aldehyde. Wherever possible, give also the common name.
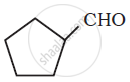
Write the IUPAC name of the following ketone or aldehyde. Wherever possible, give also the common name.
PhCOPh
Draw the structure of the given derivative.
The 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazone of benzaldehyde
Draw the structure of the given derivative.
Cyclopropanone oxime
Draw the structure of the given derivative.
Acetaldehydedimethylacetal
Draw the structure of the given derivative.
The semicarbazone of cyclobutanone
Draw the structure of the given derivative.
The ethylene ketal of hexan-3-one
Draw the structure of the given derivative.
The methyl hemiacetal of formaldehyde
Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with the following reagents.
PhMgBr and then H3O+
Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with the following reagent.
Tollens’ reagent
Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with the following reagents.
Semicarbazide and weak acid
Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with the following reagents.
Excess ethanol and acid
Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with the following reagents.
Zinc amalgam and dilute hydrochloric acid
Which of the following compounds would undergo aldol condensation, which the Cannizzaro reaction and which neither? Write the structures of the expected products of aldol condensation and Cannizzaro reaction.
- Methanal
- 2-Methylpentanal
- Benzaldehyde
- Benzophenone
- Cyclohexanone
- 1-Phenylpropanone
- Phenylacetaldehyde
- Butan-1-ol
- 2, 2-Dimethylbutanal
How will you convert ethanal into the following compound?
Butane-1, 3-diol
How will you convert ethanal into the following compound?
But-2-enal
How will you convert ethanal into the following compound?
But-2-enoic acid
Write structural formulas and names of four possible aldol condensation products from propanal and butanal. In each case, indicate which aldehyde acts as nucleophile and which as electrophile.
An organic compound with the molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollens’ reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
An organic compound (A) (molecular formula C8H16O2) was hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid produced (B). (C) on dehydration gives but-1-ene. Write equations for the reactions involved.
Acetaldehyde, Acetone, Di-tert-butyl ketone, Methyl tert-butyl ketone (reactivity towards HCN)
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH, CH3CH2CH2COOH (acid strength)
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
Benzoic acid, 4-Nitrobenzoic acid, 3, 4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength)
Propanal and Propanone
Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
Acetophenone and Benzophenone
Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
Phenol and Benzoic acid
Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate
Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
Give a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds:
Ethanal and Propanal
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
Methyl benzoate
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
m-Nitrobenzoic acid
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
p-Nitrobenzoic acid
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
Phenylacetic acid
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
p-Nitrobenzaldehyde
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Propanone to Propene
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Benzene to m-Nitroacetophenone
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Benzaldehyde to Benzophenone
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Bromobenzene to 1-Phenylethanol
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Benzaldehyde to 3-Phenylpropan-1-ol
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Benzoic acid to m-Nitrobenzyl alcohol
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Benazaldehyde to α-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
Describe the following:
Acetylation
Describe the following:
Cannizzaro reaction
Describe the following:
Cross aldol condensation
Describe the following:
Decarboxylation
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
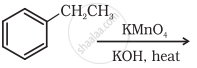
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
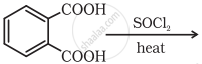
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
\[\ce{C6H5CHO ->[H2NCONHNH2]}\]
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
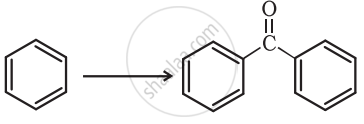
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
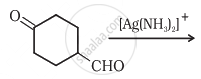
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.

Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C6H5CHO}\phantom{............}\\
\phantom{........}\ce{+\phantom{......}\ce{->[dil.NaOH][\Delta]}}\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3CH2CHO}\phantom{............}
\end{array}\]
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
\[\ce{CH3COCH2COOC2H5 ->[(i) NaBH4][(ii) H+]}\]
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
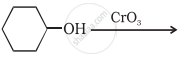
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.

Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
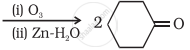
Give plausible explanation for the following:
Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2, 2, 6 trimethylcyclohexanone does not.
Give plausible explanation for the following:
There are two −NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones.
Give plausible explanation for the following:
During the preparation of esters from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, the water or the ester should be removed as soon as it is formed.
An organic compound contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen and rest oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It does not reduce Tollens’ reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogensulphite and give positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation it gives ethanoic and propanoic acid. Write the possible structure of the compound.
Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Give two reasons.
Solutions for 12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC 12 (Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids are Introduction of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids, Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones, Nature of Carbonyl Group, Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones, Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Addition Reactions, Uses of Aldehydes and Ketones, Introduction of Carboxylic Acids, Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids, Structure of the Carboxyl group, Methods of Preparation of Carboxylic Acids, Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids, Uses of Carboxylic Acids, Preparation of Aldehydes, Preparation of Ketones, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Reduction, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Oxidation, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Reactions Due to α-hydrogen, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Other Reactions, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving Cleavege of O-H Bond, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving Cleavege of C-OH Bond, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving –COOH Group, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Substitution Reactions in the Hydrocarbon Part, Structure of the Carbonyl Group, Introduction of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids, Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones, Nature of Carbonyl Group, Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones, Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Nucleophilic Addition Reactions, Uses of Aldehydes and Ketones, Introduction of Carboxylic Acids, Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids, Structure of the Carboxyl group, Methods of Preparation of Carboxylic Acids, Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids, Uses of Carboxylic Acids, Preparation of Aldehydes, Preparation of Ketones, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Reduction, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Oxidation, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Reactions Due to α-hydrogen, Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones - Other Reactions, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving Cleavege of O-H Bond, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving Cleavege of C-OH Bond, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Reactions Involving –COOH Group, Chemical Reactions of Carboxylic Acids - Substitution Reactions in the Hydrocarbon Part, Structure of the Carbonyl Group.
Using NCERT Chemistry [English] Class 12 solutions Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Chemistry [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 12, Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Chemistry [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
![NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 12 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Shaalaa.com](/images/9788174506481-chemistry-english-class-12_6:a55896f658974483bc7dc0613af00ce2.jpg)
