Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
An organic compound (A) (molecular formula C8H16O2) was hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid produced (B). (C) on dehydration gives but-1-ene. Write equations for the reactions involved.
Solution
- An organic compound A with molecular formula C8H16O2 gives a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C) on hydrolysis with dilute sulphuric acid. Thus, compound A must be an ester.
- Further, alcohol C gives acid B on oxidation with chromic acid. Thus, B and C must contain an equal number of carbon atoms. Since compound A contains a total of 8 carbon atoms, each of B and C contains 4 carbon atoms.
- Again, on dehydration, alcohol C gives but-1-ene. Therefore, C is of straight chain and hence, it is butan-1-ol. On oxidation, Butan-1-ol gives butanoic acid. Hence, acid B is butanoic acid.
Hence, the ester with molecular formula C8H16O2 is butylbutanoate.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{O}\phantom{.......}\\
||\phantom{.......}\\
\ce{\underset{Butylbutanoate}{CH3CH2CH2 - C - OCH2CH2CH2CH3}}\
\end{array}\]
All the given reactions can be explained by the following equations:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{O}\phantom{..............................................}\ce{O}\phantom{...............}\\
||\phantom{...............................................}||\phantom{...............}\\
\ce{\underset{(A)}{\underset{Butylbutanoate}{CH3CH2CH2 - C - OCH2CH2CH2CH3}} ->[dil. H2SO4] \underset{(B)}{\underset{Butanoic acid}{CH3CH2CH2 - C - OH}} + \underset{(C)}{\underset{Butan-1-ol}{CH3CH2CH2CH2OH}}}\
\end{array}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{................................................}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{................................................}||\\
\ce{CH3CH2CH2CH2 - OH ->[CrO3/CH3COOH][Oxidation] \underset{(B)}{\underset{Butanoic acid}{CH3CH2CH2 - C - OH}}}
\end{array}\]
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2CH2 - OH ->[Dehydration][-H2O] \underset{But-1-ene}{CH3CH2CH = CH2}}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
On acid hydrolysis, propane nitrile gives.
Identify ‘A' and ‘B’ in the following reaction :
C6H5MgBr + C02 `(`> ‘A’ `(PCl_5)/()`> ‘B’
Write the structures of A and B in the following reactions
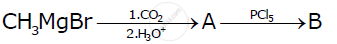
Show how the following compound can be converted to benzoic acid.
Phenylethene (Styrene)
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
Methyl benzoate
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
m-Nitrobenzoic acid
How will you prepare the given compound from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom.
p-Nitrobenzoic acid
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Benazaldehyde to α-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
How is methoxy benzene prepared from carbolic acid?
The reagent which does not react with both, acetone and benzaldehyde.
Which is the most suitable reagent for the following conversion?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{....................}\ce{O}\phantom{.....................................}\ce{O}\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{....................}||\phantom{......................................}||\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - CH = CH - CH2 - C - CH3 -> CH3 - CH = CH - CH2 - C - OH}\phantom{.}
\end{array}\]
Assertion: Aldehydes and ketones, both react with Tollen’s reagent to form silver mirror.
Reason: Both, aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group.
Substitution of one alkyl group by replacing hydrogen of primary amines
Match List - I with List - II.
| List - I | List - II | ||
| (a) |  \[\ce{->[CO,HCl][Anhyd. AlCl3/CuCl]}\] \[\ce{->[CO,HCl][Anhyd. AlCl3/CuCl]}\] |
(i) | Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction |
| (b) |
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{O}\phantom{.................}\\ ||\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{R - C - CH3 + NaOX ->} \end{array}\] |
(ii) | Gattermann-Koch reaction |
| (c) | \[\ce{R - CH2 - OH + R'COOH ->[Conc. H2SO4]}\] | (iii) | Haloform reaction |
| (d) | \[\ce{R - CH2COOH ->[(i) X2/Red P][(ii) H2O]}\] | (iv) | Esterification |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
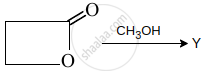
Y is:
Hex-4-ene-2-ol on treatment with PCC gives 'A'. 'A' on reaction with sodium hypoiodite gives 'B', which on further heating with soda lime gives 'C. The compound 'C' is ______.
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate words from those given in the brackets:
[stable, low, aldehyde, unstable, 6, 4, ethane, Clemmensen’s, 2, 3, carboxylic acid, high, propane, Rosenmund's]
The primary alcohols are easily oxidised first into ______ and then into ______.
