Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe the following:
Decarboxylation
Solution
Carboxylic acids lose carbon dioxide to form hydrocarbons when their sodium salts are heated with sodalime (NaOH and CaO in the ratio of 3 : 1). The reaction is known as decarboxylation.
\[\ce{R-COONa ->[NaOH and CaO][Heat]R - H + Na2CO3}\]
Alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids also undergo decarboxylation on electrolysis of their aqueous solutions and form hydrocarbons having twice the number of carbon atoms present in the alkyl group of the acid. The reaction is known as Kolbe electrolysis.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Predict the products of the following reactions :
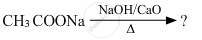
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
Write the reactions involved Decarboxylation reaction
Give a reason for the following :
N-N bond is weaker than the P-P bond.
Which of the following is the strongest acid?
Which will undergo decarboxylation rapidly?
Maximum decarboxylation occurs in:
Identify product A in the following reaction.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{COOH}\phantom{.......}\\
/\phantom{...............}\\
\ce{CH2 ->[\Delta] CH3COOH + A}\\
\backslash\phantom{................}\\
\ce{COOH}\phantom{........}
\end{array}\]
Give the order of decarboxylation of the following acid:
| CH3COOH | CH2 = CH–CH2 – COOH |
| I | II |
| CH2(COOH)2 | 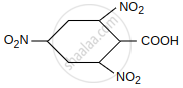 |
| III | IV |
