Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
C6H5 – O – C7H15(n−)
Solution
1-Phenoxyheptane
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound:
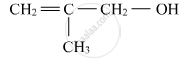
Name the following compound according to IUPAC system.
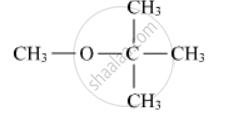
Write structures of the compounds whose IUPAC names are as follows:
3-Chloromethylpentan-1-ol.
Give IUPAC name of the following ether:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C2H5OCH2 - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\phantom{.......}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
Ethylidene dichloride when boiled with aqueous solution of NaOH yields _______.
(A) formaldehyde
(B) acetaldehyde
(C) acetone
(D) ethyl methyl ketone
Natalite is a mixture of
(a) diethyl ether and methanol
(b) diethyl ether and ethanol
(c) dimethyl ether and methanol
(d) dimethyl ether and ethanol
Give reasons Fluoride ion has higher hydration enthalpy than chloride ion.
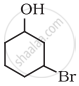
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
Isopropyl alcohol on oxidation forms:
An example of a compound with functional group – O – is ____________.
n-Propyl alcohol and isopropyl alcohol can be chemically distinguished by which reagent?
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of acidity.
\[\ce{H2O, ROH, HC ≡ CH}\]
Match the structures of the compounds given in Column I with the name of the compounds given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | 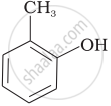 |
(a) Hydroquinone |
| (ii) | 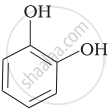 |
(b) Phenetole |
| (iii) | 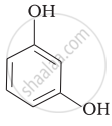 |
(c) Catechol |
| (iv) | 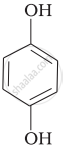 |
(d) o-Cresol |
| (v) | 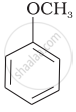 |
(e) guinone |
| (vi) | 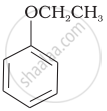 |
(f) Resorcinol |
| (g) Anisole |
Match the starting materials given in Column I with the products formed by these (Column II) in the reaction with HI.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | CH3—O—CH3 | (a) | 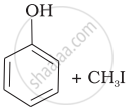 |
| (ii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{..................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.............}\\ \ce{CH-O-CH3}\\ /\phantom{..............}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{..................} \end{array}\] |
(b) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{....}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3-C-I + CH3OH}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{....} \end{array}\] |
| (iii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\\ |\phantom{....}\\ \ce{H3C-C-O-CH3}\\ |\phantom{....}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{..} \end{array}\] |
(c) | 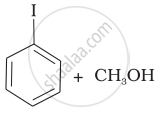 |
| (iv) | 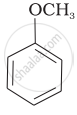 |
(d) | CH3—OH + CH3—I |
| (e) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH-OH + CH3I}\\ /\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................} \end{array}\] |
||
| (f) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH-I + CH3OH}\\ /\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................} \end{array}\] |
||
| (g) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{....}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3-C-OH + CH3I}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{....} \end{array}\] |
Assertion: p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol.
Reason: Nitro group helps in the stabilisation of the phenoxide ion by dispersal of negative charge due to resonance.
Assertion: IUPAC name of the compound
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH - O - CH2 - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{....................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}
\end{array}\] is 2-Ethoxy-2-methylethane.
Reason: In IUPAC nomenclature, ether is regarded as hydrocarbon derivative in which a hydrogen atom is replaced by —OR or —OAr group [where R = alkyl group and Ar = aryl group]
Assertion: Like bromination of benzene, bromination of phenol is also carried out in the presence of Lewis acid.
Reason: Lewis acid polarises the bromine molecule.
Write chemical reactions for the following conversion:
Acetic acid into ethyl alcohol
