Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Solutions
3: Electrochemistry
4: Chemical Kinetics
5: Surface Chemistry
6: General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
7: The p-block Elements
8: The d-block and f-block Elements
9: Coordinate Compounds
▶ 10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
13: Amines
14: Biomolecules
15: Polymers
16: Chemistry in Everyday Life
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 10 of CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC NCERT for Chemistry [English] Class 12.
NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Intext Questions [Pages 163 - 307]
Write the structure of the following compound:
2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
Write the structure of the following compound:
1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
Write the structure of the following compound:
4-tert. Butyl-3-iodoheptane
Write the structure of the following compound:
1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
Write the structure of the following compound:
1-Bromo-4-sec. butyl-2-methylbenzene
Why is sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI?
Write structures of different dihalogen derivatives of propane.
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields a single monochloride.
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields three isomeric monochlorides.
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields four isomeric monochlorides.
Draw the structure of major monohalo products in the following reaction:

Draw the structure of major monohalo products in the following reaction:
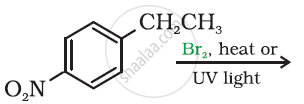
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reaction:
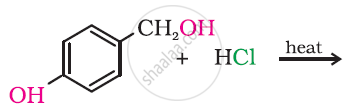
Draw the structure of major monohalo products in the following reaction:
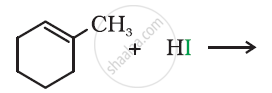
Draw the structure of major monohalo products in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br + NaI ->}\]
Draw the structure of major monohalo products in the following reaction:
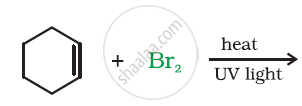
Arrange the set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points.
Bromomethane, Bromoform, Chloromethane, Dibromomethane.
Arrange the set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points.
1-Chloropropane, Isopropyl chloride, 1-Chlorobutane.
Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br or \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3CH2CHCH3}\\
\phantom{...}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{Br}\
\end{array}\]
In the following pair of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes a faster SN1 reaction?
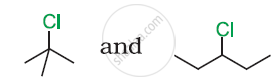
In the following pair of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes a faster SN1 reaction?
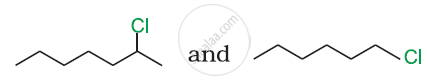
Identify A, B, C, D, E, R and R1 in the following:

NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Exercises [Pages 310 - 311]
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
(CH3)2CHCH(Cl)CH3
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH(C2H5)Cl
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
CH3CH2C(CH3)2CH2I
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
(CH3)3CCH2CH(Br)C6H5
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
CH3CH(CH3)CH(Br)CH3
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
CH3C(C2H5)2CH2Br
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
CH3C(Cl)(C2H5)CH2CH3
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
CH3CH=C(Cl)CH2CH(CH3)2
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
CH3CH=CHC(Br)(CH3)2
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
p-ClC6H4CH2CH(CH3)2
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
m-ClCH2C6H4CH2C(CH3)3
Name the following halide according to the IUPAC system and classify it as an alkyl, allyl, benzoyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
o-Br-C6H4CH(CH3)CH2CH3
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
CH3CH(Cl)CH(Br)CH3
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
CHF2CBrClF
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
ClCH2C≡CCH2Br
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
(CCl3)3CCl
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
CH3C(p-ClC6H4)2CH(Br)CH3
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound:
(CH3)3CCH=CClC6H4I-p
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
p-Bromochlorobenzene
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-1-iodooctane
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
2-Bromobutane
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
Write the structure of the following compound:
1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
Which one of the following has the highest dipole moment?
CH2Cl2
CHCl3
CCl4
A hydrocarbon C5H10 does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro compound C5H9Cl in bright sunlight. Identify the hydrocarbon.
Write the isomers of the compound having the formula C4H9Br.
Write the equation for the preparation of 1-iodobutane from 1-butanol.
Write the equation for the preparation of 1-iodobutane from 1-chlorobutane.
Write the equation for the preparation of 1-iodobutane from but-1-ene.
What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example.
Which compound in the following pair will react faster in SN2 reaction with OH−?
CH3Br or CH3I
Which compound in the following pair will react faster in SN2 reaction with OH−?
(CH3)3CCl or CH3Cl
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halide with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
1-Bromo-1-methylcyclohexane
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halide with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
2-Chloro-2-methylbutane
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halide with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
2, 2, 3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Benzene to biphenyl
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Ethanol to but-1-yne
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Ethane to bromoethene
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Propene to 1-nitropropane
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Toluene to benzyl alcohol
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Propene to propyne
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Ethanol to ethyl fluoride
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Bromomethane to propanone
How will you bring about the following conversion?
But-1-ene to but-2-ene
How will you bring about the following conversion?
1-Chlorobutane to n-octane
Explain why alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water?
Explain why Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions?
Give the uses of freon 12.
Give the uses of DDT.
Give the uses of carbon tetrachloride.
Give the uses of iodoform.
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2Cl + NaI ->[acetone][heat]}\]
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{(CH3)3CBr + KOH ->[ethanol][heat]}\]
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH(Br)CH2CH3 + NaOH ->[water]}\]
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2Br + KCN ->[aq.ethanol]}\]
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{C6H5ONa + C2H5Cl ->}\]
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH = CH2 + HBr->[peroxide]}\]
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH = C(CH3)2 + HBr ->}\]
Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
\[\ce{{n}BuBr + KCN ->[EtOH-H2O] {n}BuCN}\]
Arrange the compounds of the following set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
Arrange the compounds of the following set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
1-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-3-methylbutane
Arrange the compounds of the following set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
1-Bromobutane, 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane, 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane
Out of C6H5CH2Cl and C6H5CHClC6H5, which is more easily hydrolysed by aqueous KOH.
p-Dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. and lower solubility than those of o- and m-isomers. Discuss.
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Propene to propan-1-ol
How will you bring about the following conversion?
Ethanol to but-1-yne
How the following conversion can be carried out?
1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Benzyl alcohol to 2-phenylethanoic acid
How do you convert the following:
Ethanol to propanenitrile
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Aniline to chlorobenzene
How the following conversion can be carried out?
2-Chlorobutane to 3, 4-dimethylhexane
How the following conversion can be carried out?
2-Methyl-1-propene to 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Ethyl chloride to propanoic acid
How the following conversion can be carried out?
But-1-ene to n-butyliodide
How the following conversion can be carried out?
2-Chloropropane to 1-propanol
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Isopropyl alcohol to iodoform
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Chlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol
How the following conversion can be carried out?
2-Bromopropane to 1-bromopropane
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Chloroethane to butane
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Benzene to diphenyl
How the following conversions can be carried out?
tert-Butyl bromide to isobutyl bromide
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Aniline to phenylisocyanide
The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain.
Primary alkyl halide C4H9Br (a) reacted with alcoholic KOH to give compound (b). Compound (b) is reacted with HBr to give (c) which is an isomer of (a). When (a) is reacted with sodium metal it gives compound (d), C8H18 which is different from the compound formed when n-butyl bromide is reacted with sodium. Give the structural formula of (a) and write the equations for all the reactions.
Write the main products when n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH.
What happens when bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether?
What happens when chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis?
What happens when ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH?
What happens when methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether?
What happens when methyl chloride is treated with KCN?
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 ->}\]
Solutions for 10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 10 - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC 10 (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes are Introduction of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Nomenclature, Nature of C-X Bond, Physical Properties of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Reactions of Haloalkanes - Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions, R-s and D-l Configuration, Reactions of Haloarenes - Nucleophilic Substitution, Polyhalogen Compounds, Reactions of Haloarenes - Reaction with Metals, Reactions of Haloalkanes - Elimination Reactions, Classification of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Reactions of Haloalkanes - Reaction with Metals, Reactions of Haloarenes - Electrophilic Substitution Reactions, Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Numericals, Methods of Preparation of Haloalkanes, Methods of Preparation of Haloarenes, Introduction of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Nomenclature, Nature of C-X Bond, Physical Properties of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Reactions of Haloalkanes - Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions, R-s and D-l Configuration, Reactions of Haloarenes - Nucleophilic Substitution, Polyhalogen Compounds, Reactions of Haloarenes - Reaction with Metals, Reactions of Haloalkanes - Elimination Reactions, Classification of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, Reactions of Haloalkanes - Reaction with Metals, Reactions of Haloarenes - Electrophilic Substitution Reactions, Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Numericals, Methods of Preparation of Haloalkanes, Methods of Preparation of Haloarenes.
Using NCERT Chemistry [English] Class 12 solutions Haloalkanes and Haloarenes exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC Chemistry [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 10, Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Chemistry [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
![NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 10 - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NCERT solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 10 - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - Shaalaa.com](/images/9788174506481-chemistry-english-class-12_6:a55896f658974483bc7dc0613af00ce2.jpg)
