Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
p-Dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. and lower solubility than those of o- and m-isomers. Discuss.
Why p-dichlorobenzene has higher melting point than those of ortho and meta-isomers?
p-Dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. than those of o- and m-isomers. Discuss.
Solution
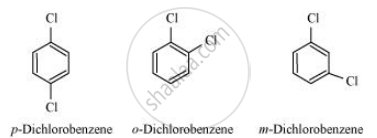
p-Dichlorobenzene is more symmetrical than o-and m-isomers. For this reason, it fits more closely than o-and m-isomers in the crystal lattice. Therefore, more energy is required to break the crystal lattice of p-dichlorobenzene. As a result, p-dichlorobenzene has a higher melting point and lower solubility than o-and m-isomers.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain why alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water?
Why dextro and laevorotatory isomers of Butan-2-ol are difficult to separate by fractional distillation?
For the same alkyl group, an alkyl bromide has a higher boiling point than alkyl fluoride because:
Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point?
How many structural isomers are possible for a compound with the molecular formula C3H7Cl?
p-dichlorobenzene has a higher melting point than its o- and m-isomers because ____________.
Reaction of \[\ce{C6H5CH2Br}\] with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows ______.
Which of the following compounds will have the highest melting point and why?
| (I) |  |
|
(II) |
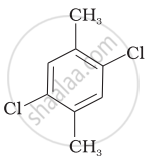 |
| (III) | 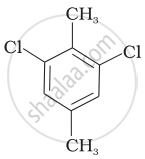 |
Why alkyl halides though polar are immiscible with water?
Why is the boiling point of o-dichlorobenzene higher than p-dichlorobenzene, but the melting point of para-isomer is higher than ortho-isomer?
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
