Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2022-2023
Date & Time: 28th February 2023, 10:30 am
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions carefully.
- There are 35 questions in this question paper with internal choice. All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper is divided into FIVE sections: Section A, B, C, D and E.
- SECTION A - question number 1 to 18 are Multiple Choice (MCQ) type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- SECTION B question number 19 to 25 are Very Short Answer (VSA) type questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION C - question number 26 to 30 are Short Answer (SA) type questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION D question number 31 and 32 are case-based questions carrying 4 marks each.
- SECTION E question number 33 to 35 are Long Answer (LA) questions carrying 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 2 questions in Section B, 2 questions in Section C, 2 questions in Section D and 2 questions in section E.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed
Auto-oxidation of chloroform in air and sunlight produces a poisonous gas known as ______.
Tear gas
Mustard gas
Phosgene gas
Chlorine gas
Phosphine
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Which among the following is an ambidentate ligand?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{COO-}\\
|\phantom{.....}\\
\ce{COO-}
\end{array}\]
\[\ce{NO^-_2}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{\overset{\bullet\bullet}{N}H3}
\end{array}\]
H2O
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Among the following, which has the highest value of pKb?
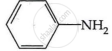
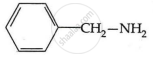
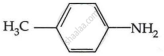
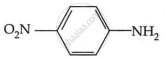
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
The slope in the plot of `log ["R"]_0/(["R"])` Vs. time for a first-order reaction is ______.
`(+"k")/2.303`
+k
`(-"k")/2.303`
−k
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
When D-glucose reacts with HI, it forms ______.
Gluconic acid
n-hexane
Saccharic acid
Iodohexane
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Inversion of configuration occurs in ______.
SN2 reaction
SN1 reaction
Neither SN2 nor SN1 reaction
SN1 as well as SN2 reaction
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Solubility of gas in liquid decreases with increase in ______.
Pressure
Temperature
Volume
Number of solute molecules
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Which of the following relations is incorrect?
R = `1/"k"("l"/"a")`
G = `"k"("a"/"l")`
G = `"k"("l"/"a")`
∧m = `"k"/"c"`
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
The reagent that can be used to distinguish acetophenone and benzophenone is ______.
2, 4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine
aqueous NaHSO3
Fehling solution
I2 and NaOH
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Which of the following is most reactive in nucleophilic addition reactions?
HCHO
CH3CHO
CH3COCH3
CH3COC2H5
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Which of the following compounds will undergo self-condensation in the presence of dilute NaOH solution?
C6H5CHO
CH3CH2CHO
(CH3)3C – CHO
H – CHO
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
For the reaction \[\ce{3A -> 2B}\], rate of reaction `-("d"["A"])/"dt"` is equal to ______.
`(+3)/2 ("d"["B"])/"dt"`
`(+2)/3 ("d"["B"])/"dt"`
`(+1)/3 ("d"["B"])/"dt"`
`(+1)/2 ("d"["B"])/"dt"`
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Which of the following transition metals shows +1 and +2 oxidation states?
Mn
Zn
Sc
Cu
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
The formula of the complex Iron (III) hexacyanidoferrate(II) is ______.
Fe2 [Fe(CN)6]3
Fe4 [Fe(CN)6]3
Fe [Fe(CN)6]
Fe3 [Fe(CN)6]2
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Assertion (A): The enthalpy of mixing Δmix H is equal to zero for an ideal solution.
Reason (R): For an ideal solution the interaction between solute and solvent molecules is stronger than the interactions between solute-solute or solvent-solvent molecules.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Assertion (A): Molar conductivity decreases with increase in concentration.
Reason (R): When concentration approaches zero, the molar conductivity is known as limiting molar conductivity.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Assertion (A): Transition metals show their highest oxidation state with oxygen.
Reason (R): The ability of oxygen to form multiple bonds to metals.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Assertion: Chlorobenzene is resistant to nucleophilic substitution reaction at room temperature.
Reason (R): C–Cl bond gets weaker due, to resonance.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
The two strands in DNA are not identical but are complementary. Explain.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Do the following conversions in not more than two steps:
CH3COOH to CH3COCH3
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Do the following conversions in not more than two steps:
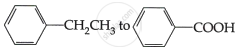
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
The conversion of molecules A to B follow second order kinetics. If concentration of A is increased to three times, how will it affect the rate of formation of B?
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Explain pseudo-first-order reaction with an example.
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
Write the IUPAC name of the following:
[Co(NH3)5(ONO)]2+
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Write the IUPAC name of the following:
K2[NiCl4]
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Advertisements
What is a chelate complex? Give one example.
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
What are Heteroleptic complexes?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Write the equation involved in the following reaction:
Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Write the chemical equation involved in the following reactions:
Acetylation of salicylic add
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Do the following conversions in not more than two steps:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3CN to CH3 - C - CH3}\\
\phantom{...........}||\\
\phantom{...........}\ce{O}
\end{array}\]
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Do the following conversions in not more than two steps:

Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write two differences between DNA and RNA.
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
\[\ce{2CH3CH2OH ->[H^+][413 K] CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH3 + H2O}\]
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Why ortho-nitrophenol is steam volatile while para-nitrophenol is not?
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
What happens when Anisole is treated with CH3Cl/anhydrous AlCl3?
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
What happens when Phenol is oxidised with Na2Cr2O7/H+?
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
What happens when (CH3)3 C – OH is heated with Cu/573 K?
Write the chemical equation in support of your answer.
Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Which isomer of C5H10 gives a single monochloro compound C5H9Cl in bright sunlight?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of reactivity towards SN2 reaction.
2-Bromopentane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
p-Dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. and lower solubility than those of o- and m-isomers. Discuss.
Chapter: [0.06] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Identify A and B in the following:

Chapter: [0.07] Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
A first-order reaction is 50% complete in 30 minutes at 300 K and in 10 minutes at 320 K. Calculate activation energy (Ea) for the reaction. [R = 8.314 J K−1 mol−1]
[Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021]
Chapter: [0.03] Chemical Kinetics
When 19.5 g of F – CH2 – COOH (Molar mass = 78 g mol−1), is dissolved in 500 g of water, the depression in freezing point is observed to be 1°C. Calculate the degree of dissociation of F – CH2 – COOH.
[Given: Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol−1]
Chapter: [0.01] Solutions
Draw the geometrical isomers of [Co(en)2Cl2]2+. Which geometrical isomer of [Co(en)2Cl2]2+ is not optically active and why?
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
Write the hybridisation and magnetic behaviour of [CoF6]3−.
[Given: Atomic number of Co = 27]
Chapter: [0.05] Coordination Compounds
The following questions are case-based questions. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
| The carbon-oxygen double bond is polarised in aldehydes and ketones due to higher electronegativity of oxygen relative to carbon. Therefore, they undergo nucleophilic addition reactions with a number of nucleophiles such as HCN, NaHSO3, alcohols, ammonia derivatives and Grignard reagents. Aldehydes are easily oxidised by mild oxidising agents as compared to ketones. The carbonyl group of carboxylic acid does not give reactions of aldehydes and ketones. Carboxylic acids are considerably more acidic than alcohols and most of simple phenols. |
Answer the following:
(a) Write the name of the product when an aldehyde reacts with excess alcohol in the presence of dry HCl. (1)
(b) Why carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol? (1)
(c) (i) Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity towards CH3MgBr: (1)
CH3CHO, \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{(CH3)3C-C-CH3}\\
\phantom{....}||\\
\phantom{....}\ce{O}
\end{array}\], \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3-C-CH3}\\
||\\
\ce{O}
\end{array}\]
(ii) Write a chemical test to distinguish between propanal and propanone. (1)
OR
(c) Write the main product in the following: (2)
| (i) | 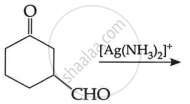 |
| (ii) | 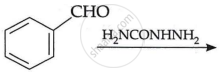 |
Chapter: [0.08] Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
The following questions are case-based questions. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow:
| Carbohydrates are optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones. They are also called saccharides. All those carbohydrates which reduce Fehling's solution and Tollen's reagent are referred to as reducing sugars. Glucose, the most important source of energy for mammals, is obtained by the hydrolysis of starch. Vitamins are accessory food factors required in the diet. Proteins are the polymers of α-amino acids and perform various structural and dynamic functions in the organisms. Deficiency of vitamins leads to many diseases. |
Answer the following:
(a) The penta-acetate of glucose does not react with Hydroxylamine. What does it indicate? (1)
(b) Why cannot vitamin C be stored in our body? (1)
(c) Define the following as related to proteins: (2)
- Peptide linkage
- Denaturation
OR
(c) Define the following as related to carbohydrates: (2)
- Anomers
- Glycosidic linkage
Chapter: [0.1] Biomolecules
Advertisements
Account for the following:
E° value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that for Cr3+/Cr2+.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Account for the following:
Sc3+ is colourless whereas Ti3+ is coloured in an aqueous solution.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
How do you prepare:
Actinoid elements show wide range of oxidation states.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Indicate the steps in the preparation of KMnO4 from pyrolusite ore.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Account for the following:
Transition metals form alloys.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Account for the following:
Ce4+ is a strong oxidising agent.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Write one similarity and one difference between the chemistry of lanthanoid and actinoid elements.
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Complete the following ionic equation:
\[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}7 + 2OH^- ->}\]
Chapter: [0.04] d-block and f-block Elements
Account for the following:
Although the amino group is o, p-directing in aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions, aniline on nitration gives a substantial amount of m-nitroaniline.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons:
(CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in an aqueous solution.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons for the following:
Ammonolysis of alkyl halides is not a good method to prepare pure primary amines.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write the chemical equations involved in the following reactions:
Carbylamine reaction
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Illustrate the following reaction giving suitable example in each case:Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write the structures of A, B and C in the following reaction:

Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Write the structures of A, B and C in the following reaction:
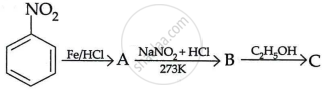
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Give reasons for the following:
Aniline does not undergo Friedel- Crafts reaction.
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Arrange the following in increasing order of their boiling point:
C2H5OH, C2H5NH2, (C2H5)3N
Chapter: [0.09] Amines
Conductivity of 2 × 10−3 M methanoic acid is 8 × 10−5 S cm−1. Calculate its molar conductivity and degree of dissociation if `∧_"m"^0` for methanoic acid, is 404 S cm2 mol−3.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Calculate the ΔrG0 and log Kc, for the given reaction at 298 K:
\[\ce{Ni_{(s)} + 2Ag^+_{( aq)} <=> Ni^{2+}_{( aq)} + 2Ag_{(s)}}\]
Given: `"E"_("Ni"^(2+)//"Ni")^0` = −0.25 V, `"E"_("Ag"^+//"Ag")^0` = +0.80 V, 1F = 96500 C mol−1.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrochemistry
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Chemistry with solutions 2022 - 2023
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 -2023 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Chemistry, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Chemistry will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
