Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following compounds will undergo self-condensation in the presence of dilute NaOH solution?
Options
C6H5CHO
CH3CH2CHO
(CH3)3C – CHO
H – CHO
Solution
CH3CH2CHO
Explanation:
Aldehydes and ketones having at least one α-hydrogen undergo a reaction in the presence of dilute alkali as catalyst to form β-hydroxy aldehydes (aldol) or β-hydroxy ketones (ketol), respectively. This is known as Aldol reaction.
Because of the presence of α-hydrogen, CH3CH2CHO undergoes an aldol reaction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A compound 'A' of molecular formula C2H3OCl undergoes a series of reactions as shown below. Write the structures of A, B, C and D in the following reactions :
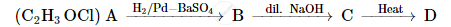
Write the products formed when CH3CHO reacts with the following reagents: CH3CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH
How will you convert ethanal into the following compound?
But-2-enal
How will you bring about the following conversion in not more than two steps?
Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal
Complete the synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C6H5CHO}\phantom{............}\\
\phantom{........}\ce{+\phantom{......}\ce{->[dil.NaOH][\Delta]}}\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3CH2CHO}\phantom{............}
\end{array}\]
Write a chemical equation for the following reaction:
Propanone is treated with dilute Ba( OH)2.
Which of the following compounds do not undergo aldol condensation?
(i) \[\ce{CH3 - CHO}\]
(ii) 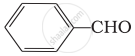
(iii) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{}||\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH3}
\end{array}\]
(iv) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CHO}\phantom{..}\\
|\phantom{...}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\\
\end{array}\]
Why are carboxylic acids more acidic than alcohols or phenols although all of them have hydrogen atom attached to a oxygen atom \[\ce{(-O-H)}\]?
Give reasons to support the answer:
Presence of Alpha hydrogen in aldehydes and ketones is essential for aldol condensation.
Identify A and B from the following reaction:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
|\phantom{....................}\\
\phantom{}\ce{2CH3 - C = O ->[Ba(OH)2] A ->[Δ] B + H2O}
\end{array}\]
