Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Reaction of \[\ce{C6H5CH2Br}\] with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows ______.
Options
SN1 mechanism
SN2 mechanism
Any of the above two depending upon the temperature of reaction
Saytzeff rule
Solution
Reaction of \[\ce{C6H5CH2Br}\] with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows SN1 mechanism.
Explanation:
Greater the stability of carbonation, greater will be its ease of formation from alkyl halide and faster will be the rate of reaction. In case of alkyl halides, 3° carbocations.
For the same reasons, allylic and benzylic halides show high reactivity towards the SN1 reaction. The carbonation thus formed gets stabilized through resonance as shown below:
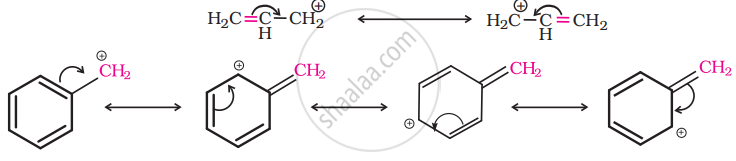
So, as the given compound, \[\ce{C6HCH2Cl}\] is a benzylic halide, it would undergo SN1 reaction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Arrange the set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points.
1-Chloropropane, Isopropyl chloride, 1-Chlorobutane.
p-Dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. and lower solubility than those of o- and m-isomers. Discuss.
Mg reacts with RBr best in ____________.
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their densities.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
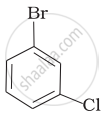
Out of o-and p-dibromobenzene which one has higher melting point and why?
Which out of the following is an intensive property?
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
Name the following halides according to the IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
\[\ce{CH3 C(C2H5)2CH2Br}\]
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
