Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Reaction of \[\ce{C6H5CH2Br}\] with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows ______.
विकल्प
SN1 mechanism
SN2 mechanism
Any of the above two depending upon the temperature of reaction
Saytzeff rule
उत्तर
Reaction of \[\ce{C6H5CH2Br}\] with aqueous sodium hydroxide follows SN1 mechanism.
Explanation:
Greater the stability of carbonation, greater will be its ease of formation from alkyl halide and faster will be the rate of reaction. In case of alkyl halides, 3° carbocations.
For the same reasons, allylic and benzylic halides show high reactivity towards the SN1 reaction. The carbonation thus formed gets stabilized through resonance as shown below:
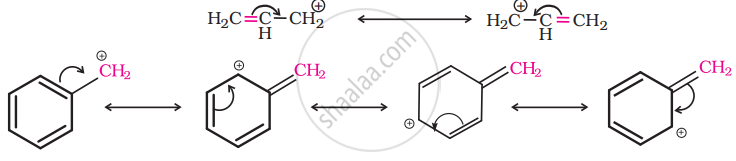
So, as the given compound, \[\ce{C6HCH2Cl}\] is a benzylic halide, it would undergo SN1 reaction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give reasons : n-Butyl bromide has higher boiling point than t-butyl bromide.
Why dextro and laevorotatory isomers of Butan-2-ol are difficult to separate by fractional distillation?
Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point?
How many structural isomers are possible for a compound with the molecular formula C3H7Cl?
Which of the following possesses the highest melting point?
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their densities.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Assertion: The boiling points of alkyl halides decrease in the order:
\[\ce{RI > RBr > RCl > RF}\]
Reason: The boiling points of alkyl chlorides, bromides and iodides are considerably higher than that of the hydrocarbon of comparable molecular mass.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CH2OH, CH3−CHO, CH3−COOH
Write the structure of the following organic halogen compound.
4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
Name the following halides according to the IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halide:
\[\ce{CH3 C(C2H5)2CH2Br}\]
