Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the following with an example.
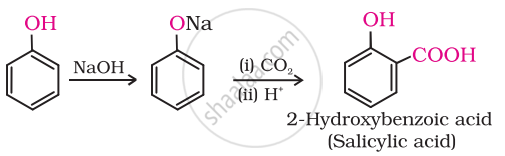
Kolbe’s reaction.
Solution
Phenoxide ion generated by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide is even more reactive than phenol towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. Hence, it undergoes electrophilic substitution with carbon dioxide, a weak electrophile. Ortho hydroxybenzoic acid is formed as the main reaction product.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the final product(s) in each of the following reactions:
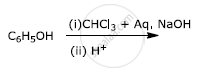
Write the main products when
2, 4, 6-trinitrochlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis
Write the main product(s) in each of the following reactions:
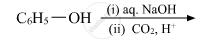
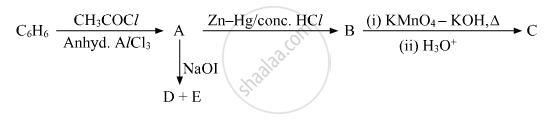
Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions:
Write the equation involved in the following reaction:
Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Write the equation involved in the following reaction:
Kolbe’s reaction
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Bromination of phenol to 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol.
Write the reaction involved in the following:
Friedal-Crafts Alkylation of Phenol
Picric acid is ____________.
When phenol is heated with CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH when salicylaldehyde is produced. This reaction is known as ____________.
On distilling phenol with Zn dust, one gets:
When Phenol is distilled with zinc dust, it gives:
The electrophile involved in Reimer-Tiemann reaction of phenol with CHCl3 in presence of NaOH:
Which of the following species can act as the strongest base?
Phenol does not undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction easily due to ______.
Convert the following:
Phenol to N-phenylethanamide.
Attacking species in nitration of benzene in presence of fuming HNO3 is
