Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why does table salt, NaCl, some times appear yellow in colour?
Solution
The yellow colour of sodium chloride is due to metal excess defect. In metal excess defect anionic vacanies are created due to diffusion of CI– to the surface of the crystal and there after unpaired electrons occupy anionic sites. These sites are called F-centres. The electrons at F-cetres then absorb energy from the visible region for the excitation which makes crystal appear yellow.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the following terms with suitable examples: F-centres
If NaCl is doped with 10−3 mol % of SrCl2, what is the concentration of cation vacancies?
Yellow colour of NaCl crystals in sodium vapour is due to ____________.
The following diagram shows:
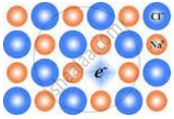
Which of the following is a non-stoichiometric defect?
Match the types of defect given in Column I with the statement given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Impurity defect | (a) NaCl with anionic sites called F-centres |
| (ii) Metal excess defect | (b) FeO with Fe3+ |
| (iii) Metal deficiency defect | (c) NaCl with Sr2+ and some cationic sites vacant |
A sample of ferrous oxide has actual formula Fe0.93O1.00. In this sample what fraction of metal ions are Fe2+ ions? What type of nonstoichiometric defect is present in this sample?
The appearance of colour in solid alkali metal halides is generally due to
The non-stoichiometric compound Fe0 940 is formed when x% of Fe2+ ions are replaced by as many `2/3` Fe3+ ions. The value of x is
Non-stoichiometric defects refer to ______
