Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Match the types of defect given in Column I with the statement given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Impurity defect | (a) NaCl with anionic sites called F-centres |
| (ii) Metal excess defect | (b) FeO with Fe3+ |
| (iii) Metal deficiency defect | (c) NaCl with Sr2+ and some cationic sites vacant |
Solution
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Impurity defect | (c) NaCl with Sr2+ and some cationic sites vacant |
| (ii) Metal excess defect | (a) NaCl with anionic sites called F-centres |
| (iii) Metal deficiency defect | (b) FeO with Fe3+ |
Explanation:
(i) Impurity defects: The defects introduced in the crystal lattice due to presence of the certain impurity are called impurity defects.
Example: Substitution of Na+ ions in NaCl by Sr2+ ions.
Structure with defect:
Impurity defect due to substitution of Na+ ions in NaCl by Sr2+ ions (Cation vacancy) ‘Schottky Defect’
(ii) When NaCl is heated in vapour of sodium some of the Cf leave their lattice site and create anion vacancies. This chloride ion wants to combine with sodium vapour to form sodium chloride. For doing so sodium atom loses electrons form Na+ ions. This released electron diffuses into the crystal to get entrapped in the anion vacancy called F-centre.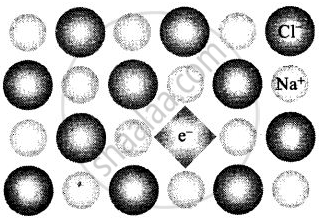
(iii) Metal deficiency is caused due to cation vacancy created by replacement of some lower valent ions by its higher valentions.
Note: Cation vacancies are found in crystals in which metals have different oxidation states.
Example: FeO, FeS, NiO
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the following terms with suitable examples: F-centres
If NaCl is doped with 10−3 mol % of SrCl2, what is the concentration of cation vacancies?
The following diagram shows:
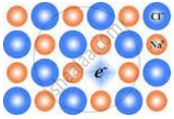
Which of the following will have metal deficiency defect?
Which of the following is a non-stoichiometric defect?
Pink colour of LiCl crystals is due to ______.
Why does table salt, NaCl, some times appear yellow in colour?
Why does white ZnO (s) becomes yellow upon heating?
On doping Ge metal with a little of In (indium), we get:
The non-stoichiometric compound Fe0 940 is formed when x% of Fe2+ ions are replaced by as many `2/3` Fe3+ ions. The value of x is
