Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Frequencies of Kα X-rays of different materials are measured. Which one of the graphs in the figure may represent the relation between the frequency v and the atomic number Z ?

Solution
Using Moseley's Law,
where v = frequency of Kα X-ray
Z = atomic number
⇒
This is the equation of a parabola with some intercept on the axis, representing atomic number (Z). Hence, curve d represent this relation correctly.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in vacuum along z-direction. What can you say about the directions of its electric and magnetic field vectors? If the frequency of the wave is 30 MHz, what is its wavelength?
The small ozone layer on top of the stratosphere is crucial for human survival. Why?
Name the electromagnetic radiations used for (a) water purification, and (b) eye surgery.
Can X-rays be used for photoelectric effect?
The energy of a photon of a characteristic X-ray from a Coolidge tube comes from
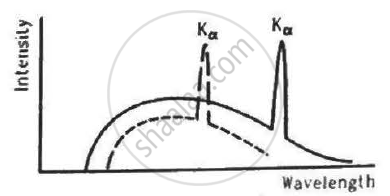
The figure shows the intensity-wavelength relations of X-rays coming from two different Coolidge tubes. The solid curve represents the relation for the tube A in which the potential difference between the target and the filament is VA and the atomic number of the target material is ZA. These quantities are VB and ZB for the other tube. Then,
Find the cutoff wavelength for the continuous X-rays coming from an X-ray tube operating at 30 kV.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The X-ray coming from a Coolidge tube has a cutoff wavelength of 80 pm. Find the kinetic energy of the electrons hitting the target.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The short-wavelength limit shifts by 26 pm when the operating voltage in an X-ray tube is increased to 1.5 times the original value. What was the original value of the operating voltage?
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
When 40 kV is applied across an X-ray tube, X-ray is obtained with a maximum frequency of 9.7 × 1018 Hz. Calculate the value of Planck constant from these data.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
State the name and the range of wavelength of the invisible electromagnetic waves beyond the red end of the visible spectrum.
Name two sources of infrared radiation.
State three properties of infrared radiations similar to that of visible light.
Answer briefly.
Can we produce a pure electric or magnetic wave in space? Why?
What are the ultraviolet rays?
Name the e.m. waves which are suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation. Write the range of frequency of these waves.
Which of the following is a tool used for separating the different color wavelengths from each other?
The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 100 W bulb at a 3 m distance is E. The electric field intensity produced by the radiations coming from 50 W bulb at the same distance is ______.
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
- λ1 is used in satellite communication.
- λ2 is used to kill germs in water purifies.
- λ3 is used to detect leakage of oil in underground pipelines.
- λ4 is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions.
- Identify and name the part of electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong.
- Arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude.
- Write one more application of each.
