Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Given below is a diagram of two systems together in the human body.
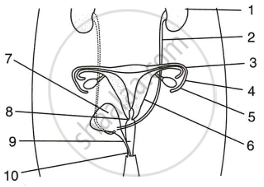 |
- Name the systems.
- Name the parts numbered 1-10.
- Describe the functions of the parts 3, 4, 5 & 6.
- What will happen if the part 3 on both sides gets blocked?
Solution
- The given system is the Urinogenital System of the human female body.
-
- Kidney
- Ureter
- Oviduct or fallopian tube
- Oviducal funnel
- Ovary
- Lining of uterus
- Urinary bladder
- Cervix
- Vagina
- Vulva
- Oviduct: Transport the ovum into the uterus; fertilisation occurs here, and the zygote travels down the uterus via the oviduct.
Oviducal funnel: The released egg is picked up by the fimbriae (cilia) of the oviducal funnel of the oviduct.
Ovary: It produces gg and the female hormones progesterone and oestrogen.
Lining of uterus: It provides a surface for the implantation of a fertilised egg. - If both Fallopian tubes are blocked, the ovary's ovum will not reach the oviduct, preventing fertilization.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the changes that take place in the uterus when Implantation of embryo has occurred
What joins embryo to placenta in mother's body?
In a flower, the parts that produce male and female gametes are respectively :
(a) sepal and anther
(b) filament and stigma
(c) anther and ovary
(d) stamen and style
What is reproduction? List its two types.
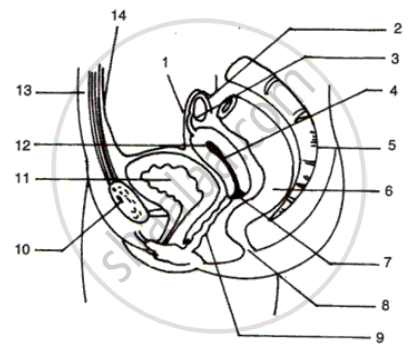
Diagram shows the reproductive system of female human beings:
(i) Name the parts numbered 1 to 14.
(ii) Normally, after how many days does an ovary release an egg?
(iii) Where are the sperms released during coitus?
(iv) What is the role of sperms after their ejaculation in vagina?
(v) What is the function of the organ numbered 5?
(vi) What is the gestation period in human?
Choose the correct answer:
Fertilization occurs in _____________
Give the functions of the following:
Vagina
Define the following:
Clone
Answer the following question.
What is contraception? List three advantages of adopting contraceptive measures.
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with a suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Acrosome
(ii) Ovulation (iii) Sperm (iv) Menopause (v) Implantation (vi) Fertilization (vii) Contraception in males |
(a) Male gamete
(b) Oviduct (c) Uterus (d) Spermatozoa (e) Progesterone (f) Stoppage of the menstrual cycle (g) Sudden change in genes |
