Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Heat energy is supplied at a constant rate to 100g of ice at 0 °C. The ice is converted into water at 0° C in 2 minutes. How much time will be required to raise the temperature of water from 0 °C to 20 °C? [Given: sp. heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 °C-1, sp. latent heat of ice = 336 J g-1].
Solution
Heat energy required to melt 100 g of ice at 0 °C is
Q = mL = 100 × 336=33600 J
Therefore, heat energy supplied per minute is
`33600/2=16800 "J min"^-1`
Now, heat energy required to raise the temperature of water from 0°C to 20°C is
Q'=mc × rise in temperature =100 × 4.2 × 20 = 8400 J
If time required for this heat gain is t minutes, then Heat energy supplied in t minutes is
`16800 xx "t"=8400`
`therefore "t" =8400/16800`
`"t" = 0.5 "min"`
`"t" = 30 "s"`
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name a liquid which has the highest specific heat capacity.
The substances like water which have ........... Heat capacity warm up more slowly than substances like iron which have .......... heat capacity.
State the condition for the flow of heat energy from one body to another.
Write the approximate values of the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam.
How much heat energy is released when 5 g of water at 20° C changes to ice at 0° C?
[Specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 ° C-1 Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J g-1]
50 g of copper is heated to increase its temperature by 10° C. If the same quantity of heat is given to 5 g water, the rise in its temperature is [Specific heat of copper = 420 joule-kg-1 °C-1 , specific heat of water = 4200 joule-kg-I °C-1]
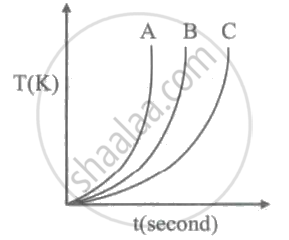
Which of the following substances (A, B and C) has the highest specific beat?
A piece of lead weighing 500 g gives out 1200 calories of heat when it is cooled from 100° C to 20° C. Find its specific heat.
Conductors have generally high specific heat capacities and insulators have low specific heat capacities.
