(English Medium)
Academic Year: 2013-2014
Date: March 2014
Advertisements
Section I is compulsory. Attempt any four questions from Section II.
A force is applied on (i) a non-rigid body and (ii) a rigid body. How does the effect of the force differ in the above two cases?
Chapter: [0.01] Force
A metallic ball is hanging by a string from a fixed support. Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the forces acting on the ball and the string.
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
What is the weight of a body placed at the centre of the earth?
Chapter: [0.01] Force
What is the principle of an ideal machine?
Chapter: [0.03] Machines
Is it possible to have an accelerated motion with a constant speed? Explain
Chapter: [0.01] Force
When does a force do work?
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
What is the work done by the moon when it revolves around the earth?
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
Calculate the change in the Kinetic energy of a moving body if its velocity is reduced to 1/3rd of the initial velocity.
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
State the energy change in the following device while in use:
A loudspeaker
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
State the energy change in the following device while in use:
A glowing electric bulb.
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
What is nuclear energy?
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
Name the process used for producing electricity using nuclear energy.
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
State one important advantage and disadvantage each of using nuclear energy for producing electricity.
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
(i) The conversion of part of the energy into an undesirable form is called ______________.
(ii) For a given height h, __________________ the length l of the inclined plane, lesser will be the effort required.
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
Draw the diagram given below and clearly show the path taken by the emergent ray.
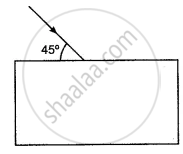
Chapter: [0.04] Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
What is consumed using different electrical appliances, for which electricity bills are paid?
Chapter: [0.08] Current Electricity
Name a common device that uses electromagnets.
Chapter: [0.1] Electro Magnetism
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Chapter: [0.04] Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
Chapter: [0.04] Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
Advertisements
Name the factors affecting the critical angle for the pair of media.
Chapter: [0.04] Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
Name a prism required for obtaining a spectrum of Ultraviolet light.
Chapter: [0.04] Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
Name the radiation which can be detected by a thermopile.
Chapter: [0.06] Spectrum
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger?
Chapter: [0.06] Spectrum
Name one property of waves that do not change when the wave passes from one medium to another.
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
Find the equivalent resistance between points A and B
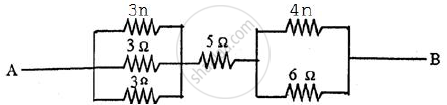
Chapter: [0.08] Current Electricity
50 g of metal piece at 27°C requires 2400 J of heat energy so as to attain a temperature of 327°C . Calculate the specific heat capacity of the metal.
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry
An electron emitter must have _____________ work function and ___________ melting point.
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
A man having a box on his head, climbs up a slope and another man having an identical box walks the same distance on a levelled road.
Who does more work against the force of gravity and why?
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
Two forces each of 5N act vertically upwards and downwards respectively on the two ends of a uniform metre rule which is placed at its mid-point as shown in the diagram. Determine the magnitude of the resultant moment of these forces about the midpoint.
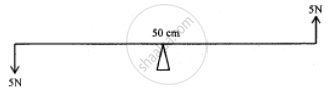
Chapter: [0.03] Machines
A body is thrown vertically upwards. Its velocity keeps on decreasing. What happens to its kinetic energy as its velocity becomes zero?
Chapter: [0.02] Work, Energy and Power
Draw a diagram to show how a single pulley can be used so as to have its ideal M.A= 2.
Chapter: [0.03] Machines
Derive a relationship between mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency of a machine.
Chapter: [0.03] Machines
Light passes through a rectangular glass slab and through a triangular glass prism. In what way does the direction of the two emergent beams differ and why?
Chapter: [0.04] Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces
Ranbir claims to have obtained an image twice the size of the object with a concave lens. Is he correct? Give a reason for your answer.
Chapter: [0.05] Refraction Through a Lense
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the image formation.
Chapter: [0.05] Refraction Through a Lense
Define the power of a lens.
Chapter: [0.05] Refraction Through a Lense
The lens mentioned in 6(b) above is of focal length 25cm. Calculate the power of the lens.
Chapter: [0.05] Refraction Through a Lense
Advertisements
The adjacent diagram shows three different modes of vibrations P, Q and R of the same string.
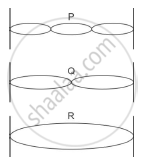
(i) Which vibration will produce a louder sound and why?
(ii) The sound of which string will have maximum shrillness?
(iii) State the ratio of wavelengths of P and R.
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
A wave has wavelength 50 Å.
- Name the wave.
- State its speed in vacuum.
- State its one use.
Chapter: [0.06] Spectrum
State one important property of waves used for echo depth sounding.
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
A radar sends a signal to an aircraft at a distance of 30 km away and receives it back after 2 x 10-4 seconds. What is the speed of the signal?
Chapter: [0.07] Sound
Two resistors of 4Ω and 6 Ω are connected in parallel to a cell to draw 0.5 A current from the cell.
(i) Draw a labelled circuit diagram showing the above arrangement.
(ii) Calculate the current in each resistor. What is an Ohmic resistor?
Chapter: [0.08] Current Electricity
What is an Ohmic resistor?
Chapter: [0.08] Current Electricity
Two copper wires are of the same length, but one is thicker than the other. Which wire will have more resistance?
Chapter: [0.08] Current Electricity
(i) Two sets A and B, of three bulbs each, are glowing in two separate rooms. When one of the bulbs in set A is fused, the other two bulbs also cease to glow. But in set B, when one bulb fuses, the other two bulbs continue to glow. Explain why this phenomenon occurs.
(ii) Why do we prefer arrangements of Set B for house circuiting?
Chapter: [0.08] Current Electricity
Heat energy is supplied at a constant rate to 100g of ice at 0 °C. The ice is converted into water at 0° C in 2 minutes. How much time will be required to raise the temperature of water from 0 °C to 20 °C? [Given: sp. heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1 °C-1, sp. latent heat of ice = 336 J g-1].
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry
Specific heat capacity of substance A is 3.8 J g-1K-1 whereas the specific heat capacity of substance B is 0.4 J g-1 K-1
(i) Which of the two is a good conductor of heat?
(ii) How is one led to the above conclusion?
(iii) If substances A and B are liquids then which one would be more useful in car radiators?
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry
State any two measures to minimize the impact of global warming.
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry [0.11] Calorimetry
What is the Greenhouse effect?
Chapter: [0.11] Calorimetry [0.11] Calorimetry
Name two factors on which the magnitude of an induced e.m.f. in the secondary coil depends.
Chapter: [0.1] Electro Magnetism
In the following diagram an arrow shows the motion of the coil towards the bar magnet.
(1) State in which direction the current flows, A to B or B to A?
(2) Name the law used to come to the conclusion.

Chapter: [0.1] Electro Magnetism
A nucleus `""_11^24Na` emits a beta particle to change into Magnesium (Mg)
(i) Write the symbolic equation for the process.
(ii) What are numbers 24 and 11 called?
(iii) What is the general name of `""_12^24Mg `with respect to `""_11^24Na` ?
Chapter: [0.12] Radioactivity
In a cathode ray tube state:
(i) the purpose of covering cathode by thorium and carbon.
(ii) the purpose of the fluorescent screen.
(iii) how is it possible to increase the rate of emission of electrons.
Chapter: [0.12] Radioactivity
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CISCE previous year question papers ICSE Class 10 Physics with solutions 2013 - 2014
Previous year Question paper for CISCE ICSE Class 10 -2014 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CISCE ICSE Class 10 .
How CISCE ICSE Class 10 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
