Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The adjacent diagram shows three different modes of vibrations P, Q and R of the same string.
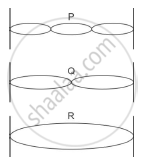
(i) Which vibration will produce a louder sound and why?
(ii) The sound of which string will have maximum shrillness?
(iii) State the ratio of wavelengths of P and R.
Solution 1
(i) The loudness or softness of a sound is determined by the amplitude (or intensity) of the wave. In this case the amplitude of R is greater than the amplitude of other vibration modes. Hence, the vibration R will produce more sound than the other two. Louder sound corresponds to the wave of larger amplitude.
(ii) Shrillness or Pitch of a note depends on the wavelength or frequency of wave and here the vibration P has m ore frequency than others. If f is the principle frequency, then
Frequency (P) = 3 f
Frequency (Q) = 2 f
Frequency (R) = f
Hence P has more shrillness than others.
(iii) If the frequency of vibration of R = f, frequency of vibration of Q = 2f, and that of P =3 f.
`Ratio f_P/f_R=3/1`
`f_P:f_R=3:1`
As `fprop1/lambda` hence `lambda_P/lambda_R=1:3`
OR (Another method)
From figure we can say that 3 vibration of P corresponds to 1 vibration of R

i.e `3lambda_P=1lambdaR`
`thereforelambda_P/lambda_R=1/3=1:3`
Therefore, ratio of wavelength of P and R is 1:3.
Solution 2
(i) Vibration R as its amplitude is high as loudness ∝ A2
(ii) Sound of string ‘P’ will have maximum shrillness as its frequency is maximum.
Pitch ∝ frequency.
(iii) λP : λR = 3 : 1
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the diagram below, A, B, C, D are four pendulums suspended from the same elastic string PQ. The length of A and C are equal to each other while the length of pendulum B is smaller than that of D. Pendulum A is set into a mode of vibrations

1) Name the type of vibrations taking place in pendulums B and D?
2) What is the state of pendulum C?
3) State the reason for the type of vibrations in pendulum B and C.
Distinguish between the free (or natural) and forced vibrations.
Resonance is a special case of ______ vibrations, when frequency of the driving force is ______ natural frequency of the body.
In Fig. A, B, C and D are four pendulums suspended from the same elastic string XY. The lengths of pendulum A and D are equal, while the length of pendulum B is shorter and of the pendulum C is longer. Pendulum A is set into vibrations.
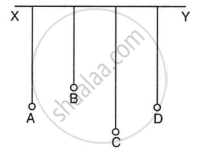
- What is your observation about the vibrations of pendulum D?
- Give reason for your observation in part (a).
- What type of vibrations take place in pendulums Band C?
- Give reason for the answer in part (c).
Differentiate between the following:
Light and sound waves.
What do you mean by resonance? When does resonance occur?
What do you understand by free vibrations of a body? Draw a displacement-time graph to represent them. Given one example.
