Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What do you mean by resonance? When does resonance occur?
Solution
Resonance is a special case of forced vibration, when a body vibrates under the influence of an external periodic force, with a very large amplitude. Resonance occurs when the frequency of external force is either equal to or is integer multiple of the natural frequency of the vibrating body.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
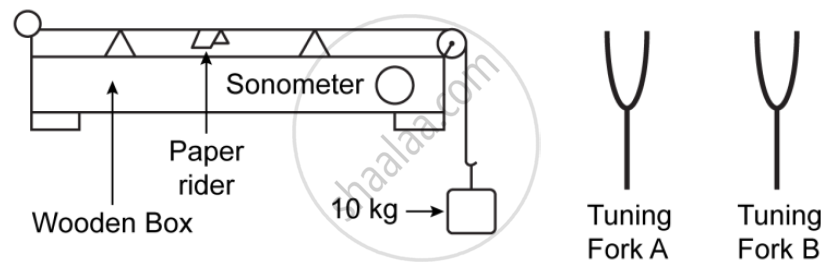
The diagram above shows a wire stretched over a sonometer. Stems of two vibrating tuning forks A and Bare touched to the wooden box of the sonometer. It is observed that the paper rider (a small piece of paper folded at the centre) present on the wire flies off when the stem of vibrating tuning fork B is touched to the wooden box but the paper just vibrates when the stem of vibrating tuning fork A is touched to the wooden box.
1) Name the phenomenon when the paper rider just vibrates.
2) Name the phenomenon when the paper rider flies off.
3) Why does the paper rider fly off when the stem of tuning fork B is touched to the box?
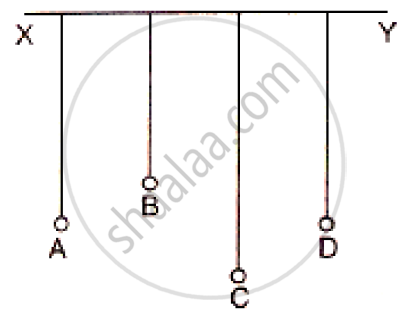
In following figure shows A, B, C and D are four pendulums suspended from the same elastic string XY. Lengths of pendulum A and D are equal, while the length of pendulum B is smaller and the pendulum C is longer. The pendulum A is set into vibration.
(a) what is your observation? (b) Give reason for your observation.
In following figure shows A, B , C and D represent test tube each of height 20 cm which are filled with water up to heights of 12 cm, 14 cm, 16cm and 18cm respectively. If a vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth if test tube D, a loud sound is heard.

- Describe the observations with the tubes A, B and C when the vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth of these tubes.
- Give the reason for your observation in each case.
- State the principle illustrated by the above experiment.
Name the phenomenon involved in tuning your radio set to a particular station and define it.
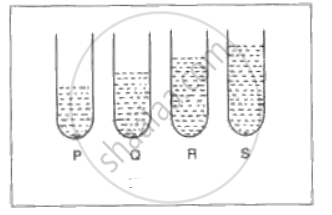
In fig. , P, Q, R and S represent test tubes each of height 20 cm which are filled with water upto heights of 10 cm, 14 cm, 16 cm and 18 cm respectively. If a vibrating tuning fork is placed over the mouth of test tube Q, a loud sound is heard.
(i) Describe the observations with the tubes P, R and S.
(ii) Give the reason for your observation in each case.
(iii) State the principle illustrated by the above experiment.
Differentiate between the following:
Radio waves and light waves.
State two ways in which resonance differs from forced vibrations.
Describe a simple experiment to illustrate the phenomenon of resonance and explain it.
