Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How did Charles's law lead to the concept of an absolute scale of temperature?
Solution
The temperature scale with its zero at -273°C and where each degree is equal to the degree on the Celsius scale is called the absolute scale of temperature.
The temperature of -273°C is called absolute zero. Theoretically, this is the lowest temperature which can never be reached. All molecular motion ceases at this temperature.
The temperature of -273°C is called absolute zero.
V = V° `((273 + "t")/273)`
Volume at - 273°C = V° `((273 - 273)/273) = 0`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
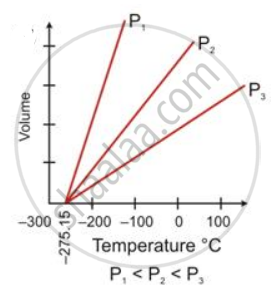
State the following:
Ice point in absolute temperature
Choose the correct answer:
The volume-temperature relationship is given by
2 liters of gas is enclosed in a vessel at a pressure of 760 mmHg. If the temperature remains constant, calculate pressure when volume changes to 4 dm3.
88 cm3 of nitrogen is at a pressure of 770 mm mercury. If the pressure is raised to 880 mmHg, find by how much the volume will diminish, the temperature remaining constant.
Calculate the final volume of a gas 'X' if the original pressure of the gas at STP is doubled and its temperature is increased three times.
An LPG cylinder can withstand a pressure of 14.9 atmospheres. The pressure gauge of the cylinder indicates 12 atmospheres at 27°C. Because of a sudden fire in the building, the temperature rises. At what temperature will the cylinder explode?
Correct the following statement:
The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature, pressure remaining constant.
According to Charles’s law, at constant pressure, the temperature is inversely proportional to volume.
The following question refers to one mole of chlorine gas.
What volume will it occupy at 273°C?
