Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How does ideal machine differ from a practical machine ?
Solution
| Ideal machine | Practical machine | |
| 1. | Efficiency is 100%. | Efficiency is less than 100%. |
| 2. | Its parts are weightless, elastic and perfectly smooth. | Its parts are not weightless, elastic or perfectly smooth. |
| 3. | There is no loss in energy due to friction. | There is always some loss of energy due to friction. |
| 4. | The work output of such a machine is equal to the work input. | Work output is always less than work input. |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What do you understand by an ideal machine?
How is mechanical advantage related to the velocity ratio for an ideal machine?
State one reason why is mechanical advantage less than the velocity ratio for an actual machine.
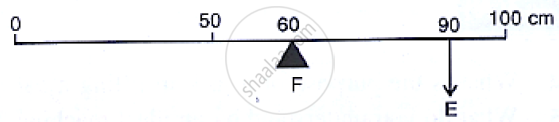
Shows a uniform metre scale of weight W supported on a fulcrum at the 60 cm mark by applying the effort E at the 90 cm mark.
- State with reason whether the weight W of the scale is greater than, less than or equal to the effort E.
- Find the mechanical advantage in an ideal case.
A pair of scissors is used to cut a piece of a cloth by keeping it at a distance 8.0 cm from its rivet and applying an effort of 10 kgf by fingers at a distance 2.0 cm from the rivet.
- Find:
- the mechanical advantage of scissors and
- the load offered by the cloth.
- How does the pair of scissors act: as a force multiplier or as speed multiplier?
The figure below shows the use of a lever.

- State the principle of moments as applied to the above lever.
- To which class of lever does it belong ? Give an example of this class of lever.
- If FA = 10 cm, AB = 490 cm calculate:
- the mechanical advantage and
- the minimum effort required to lift the load (= 50 N).
State the principle of an ideal machine.
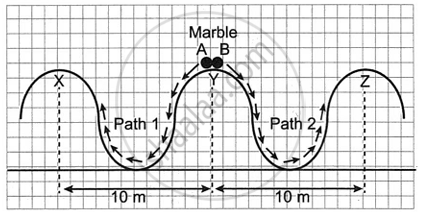
Two identical marbles A and B are rolled down along Path 1 and Path 2 respectively.
Path 1 is frictionless and Path 2 is rough.
- Which marble will surely reach the next peak?
- Along which path/s the mechanical energy will be conserved?
- Along which path/s is the law of conservation of energy obeyed?
How is mechanical advantage related to velocity ratio for a practical machine?
Give two reasons for a machine not to be 100% efficient?
