Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How does the imposition of a unit tax affect the supply curve of a firm?
Solution
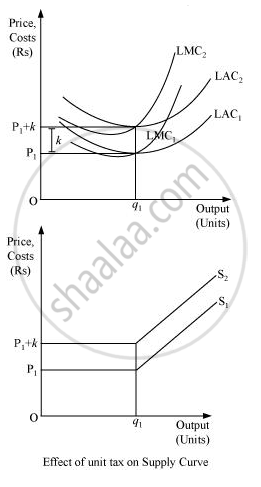
A unit tax is the tax imposed on per unit of the output sold. Due to the imposition of unit tax, the cost of production per unit of output increases, which ultimately increases the marginal cost. Consequently, the LMC curve will shift leftward upward and as the supply curve is a portion of LMC, so the supply curve will also shift leftward upward.
Let us understand the effect of imposition of unit tax through an example.
Suppose that a firm is facing the price OP1. LAC1 and LMC1 are the long run average cost curve and long run marginal cost curve respectively. Also assume that the government has imposed a unit tax of Rs k per unit of output produced. Now, this will rise the firm’s LAC and LMC, as the firm needs to pay Rs k extra on each output produced. Consequently, LMC1 and LAC1 will shift leftward upwards to LMC2 and LAC2. The magnitude of shift is equal to Rs k. As the supply curve is a part of LMC, it will also shift leftward from S1 to S2, due to the imposition of the tax. Consequently, the firm will now supply lesser units of output.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are the equilibrium price and quantity affected when both demand and supply curves shift in the same direction?
Suppose the demand and supply curves of salt are given by:
qD = 1,000 − p qS = 700 + 2p
(a) Find the equilibrium price and quantity.
(b) Now, suppose that the price of an input that used to produce salt has increased so, that the new supply curve is
qS = 400 +2p
How does the equilibrium price and quantity change? Does the change conform to your expectation?
(c) Suppose the government has imposed a tax of Rs 3 per unit of sale on salt. How does it affect the equilibrium rice quantity?
What is the supply curve of a firm in the short run?
What is the supply curve of a firm in the long run?
How does technological progress affect the supply curve of a firm?
How does an increase in the price of an input affect the supply curve of a firm?
How are the equilibrium price and quantity affected when demand and supply curves shift in opposite directions?
