Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is the supply curve of a firm in the short run?
Solution
The short run supply curve of perfect competitive firm is the summation of the upward sloping portion of SMC (above the minimum point of SAVC), when price ≥ min SAVC, and vertical portion of price-axis, when price < min SAVC.
Stage 1
When the price is greater than or equal to minimum of SAVC, i.e., P ≥ min SAVC.
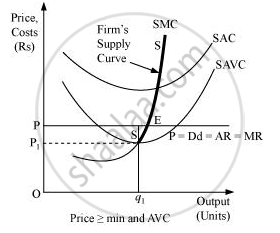
At the market price OP, the three following conditions for equilibrium are fulfilled:
-
MC = MR
-
MC is upward sloping
-
Price exceeds the minimum of SAVC
At this market price the firm is producing profit maximising output Oq1.
In this case, the supply curve of the firm is regarded as the upward sloping part of SMC (above the minimum point of SAVC), i.e. SS. When the price is greater than or equal to minimum of SAVC, the supply curve is indicated by SS.
Stage 2
When the price is less than the minimum of SAVC
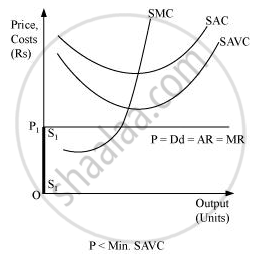
Let us suppose that the firm is facing price OP1 that is lesser than the minimum of SAVC. At this price, the firm cannot continue production as it cannot even cover up its variable costs and thereby incurs losses, which implies that the firm would produce nothing. Thus, it will incur loss that will be equivalent to its fixed costs. It will be lesser compared to the losses associated with producing any positive output level. Thus, the firm will not produce anything at this price and thereby the quantity supplied will be zero. The firm’s supply curve is indicated by the darkened vertical line S1S1.
Therefore, the short run supply curve of perfect competitive firm is (SS + S1S1).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are the equilibrium price and quantity affected when both demand and supply curves shift in the same direction?
Suppose the demand and supply curves of salt are given by:
qD = 1,000 − p qS = 700 + 2p
(a) Find the equilibrium price and quantity.
(b) Now, suppose that the price of an input that used to produce salt has increased so, that the new supply curve is
qS = 400 +2p
How does the equilibrium price and quantity change? Does the change conform to your expectation?
(c) Suppose the government has imposed a tax of Rs 3 per unit of sale on salt. How does it affect the equilibrium rice quantity?
What is the supply curve of a firm in the long run?
How does technological progress affect the supply curve of a firm?
How does the imposition of a unit tax affect the supply curve of a firm?
How does an increase in the price of an input affect the supply curve of a firm?
How are the equilibrium price and quantity affected when demand and supply curves shift in opposite directions?
