Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Will a profit-maximising firm in a competitive market produce a positive level of output in the long run if the market price is less than the minimum of AC? Give an explanation.
Solution
It is not possible for a firm to produce positive level of output in the long run if the market price falls short of the minimum of AC. This is because, in the long run there is free entry and exit of firms and all firms earn normal profit. Therefore, any firm making losses in long run will stop production.
Let us understand this concept through an example:-
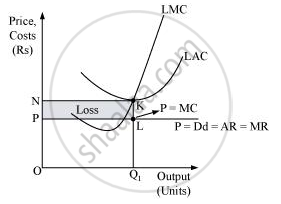
At Oq1 level of output,
Price charged by the firm = OP.
Revenue generated by the firm (TR) = P × Q
= OP × Oq1
= area (rectangle Oq1LP)
Cost of producing Oq1 level of output (TC) = LAC × Quantity of output
= ON × Oq1
TC = area (rectangle Oq1KN)
Profit earned by the firm = TR − TC
= area (rectangle Oq1LP) − area (rectangle Oq1KN)
= − area (rectangle NKLP)
Thus, the loss incurred by the firm is equal to the area of the rectangle NKLP.
In the long run, all firms earn zero economic profit, and if any firm earns loss or negative profit, then the firm will shut down its production. Thus, if the firm earns loss, i.e. if price is lesser than LAC at any level of output, it will not be the profit maximising output level of the firm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What conditions must hold if a profit-maximizing firm produces positive output in a competitive market?
Can there be a positive level of output that a profit-maximising firm produces in a competitive market at which market price is not equal to marginal cost? Give an explanation.
Will a profit-maximising firm in a competitive market ever produce a positive level of output in the range where the marginal cost is falling? Give an explanation.
Will a profit-maximising firm in a competitive market produce a positive level of output in the short run if the market price is less than the minimum of AVC?
The following table shows the total revenue and total cost schedules of a competitive firm. Calculate the profit at each output level. Determine also the market price of the good.
|
Quantity Sold |
TR (Rs.) |
TC (Rs.) |
Profit |
|
0 |
0 |
5 |
|
|
1 |
5 |
7 |
|
|
2 |
10 |
10 |
|
|
3 |
15 |
12 |
|
|
4 |
20 |
15 |
|
|
5 |
25 |
23 |
|
|
6 |
30 |
33 |
|
|
7 |
35 |
40 |
The following table shows the total cost schedule of a competitive firm. It is given that the price of the good is Rs 10. Calculate the profit at each output level. Find the profit maximising the level of output.
|
Quantity Sold |
TC (Rs.) |
|
0 |
5 |
|
1 |
15 |
|
2 |
22 |
|
3 |
27 |
|
4 |
31 |
|
5 |
38 |
|
6 |
49 |
|
7 |
63 |
|
8 |
81 |
|
9 |
101 |
|
10 |
123 |
